One Con of Reclamation: Environmental Impact Explained

Reclamation projects, while often aimed at revitalizing land and resources, come with a significant con: their environmental impact. As we strive to repurpose degraded lands or extract valuable materials, the delicate balance of ecosystems can be disrupted, leading to long-term consequences. Understanding these impacts is crucial for making informed decisions about reclamation practices. In this post, we’ll explore the environmental challenges associated with reclamation, backed by SEO-driven insights for both informational and commercial audiences. (land reclamation, environmental impact, ecosystem disruption)
Understanding the Environmental Impact of Reclamation
Reclamation involves altering natural landscapes to restore productivity or extract resources. While the goals are often beneficial, the process can harm biodiversity, soil health, and water systems. Key impacts include habitat destruction, soil erosion, and pollution. These issues not only affect local ecosystems but also contribute to broader environmental concerns like climate change. (biodiversity loss, soil erosion, pollution)
Habitat Destruction and Biodiversity Loss
Reclamation projects frequently require clearing large areas of land, displacing wildlife and destroying habitats. This disruption can lead to the decline or extinction of species, particularly those already endangered. For instance, mining reclamation often involves removing topsoil and vegetation, leaving the land barren for years. (habitat destruction, endangered species, mining reclamation)
Soil Erosion and Degradation
Reclamation activities can accelerate soil erosion, especially when vegetation is removed. Without plant roots to hold the soil in place, it becomes vulnerable to wind and water erosion. Over time, this degrades soil quality, making it less fertile and less capable of supporting new growth. (soil erosion, soil degradation, vegetation loss)
Water Systems at Risk
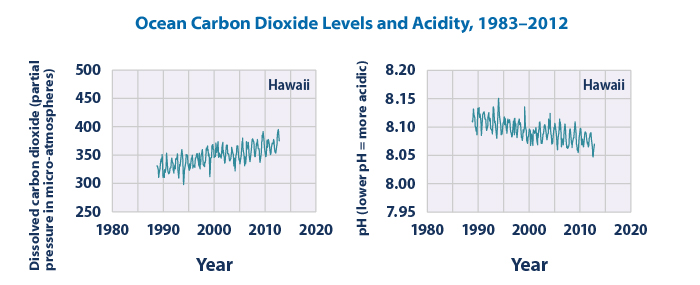
Water bodies near reclamation sites are particularly vulnerable. Sediment runoff from eroded soil can pollute rivers and lakes, harming aquatic life. Additionally, chemicals used in reclamation processes, such as those in mining or industrial sites, can contaminate groundwater and surface water. (water pollution, sediment runoff, chemical contamination)
Impact on Aquatic Ecosystems
Polluted water not only affects fish and other aquatic organisms but also disrupts the food chain. Contaminants can accumulate in predators, posing risks to humans who consume these animals. This highlights the interconnectedness of ecosystems and the far-reaching consequences of reclamation. (aquatic ecosystems, food chain disruption, water contamination)
Groundwater Contamination
Reclamation of industrial or mining sites often involves managing hazardous materials. If not properly contained, these substances can leach into groundwater, making it unsafe for consumption. This is a critical concern for communities relying on local water sources. (groundwater contamination, hazardous materials, water safety)
| Environmental Impact | Examples | Long-Term Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat Destruction | Clearing forests for mining | Loss of biodiversity |
| Soil Erosion | Removing vegetation | Reduced soil fertility |
| Water Pollution | Chemical runoff from sites | Harm to aquatic life and humans |

📌 Note: Proper planning and mitigation strategies can reduce the environmental impact of reclamation projects.
Mitigating the Environmental Impact

While reclamation can have severe environmental consequences, proactive measures can minimize harm. Sustainable practices, such as using native plants for revegetation and implementing erosion control measures, are essential. Additionally, strict regulations and monitoring can ensure that reclamation projects adhere to environmental standards. (sustainable reclamation, erosion control, environmental regulations)
Revegetation and Ecosystem Restoration
Planting native species helps restore habitats and prevent soil erosion. These plants are adapted to local conditions, increasing their chances of survival and contributing to ecosystem recovery. (revegetation, native species, ecosystem restoration)
Pollution Control Measures
Implementing systems to capture and treat runoff can prevent water pollution. Similarly, containing hazardous materials through proper waste management reduces the risk of groundwater contamination. (pollution control, waste management, water treatment)
Checklist for Environmentally Responsible Reclamation

- Assess the site’s ecological impact before starting.
- Use native plants for revegetation efforts.
- Implement erosion control measures to protect soil.
- Monitor water quality regularly to detect contamination early.
- Follow strict environmental regulations and guidelines.
Reclamation projects, while beneficial in many ways, pose significant environmental challenges. From habitat destruction to water pollution, the impacts can be far-reaching. However, by adopting sustainable practices and prioritizing ecosystem health, we can mitigate these effects and ensure that reclamation efforts contribute positively to the environment. (sustainable practices, ecosystem health, positive reclamation)
What is the biggest environmental impact of reclamation?
+
The biggest environmental impact is often habitat destruction and biodiversity loss, as reclamation projects frequently require clearing large areas of land.
How can soil erosion be prevented during reclamation?
+
Soil erosion can be prevented by using erosion control measures like retaining walls, vegetation cover, and proper land grading.
Why is water pollution a concern in reclamation projects?
+
Water pollution is a concern because sediment runoff and chemical contaminants from reclamation sites can harm aquatic ecosystems and pose risks to human health.

