Animal Cell Colors: A Visual Guide to Their Vibrancy
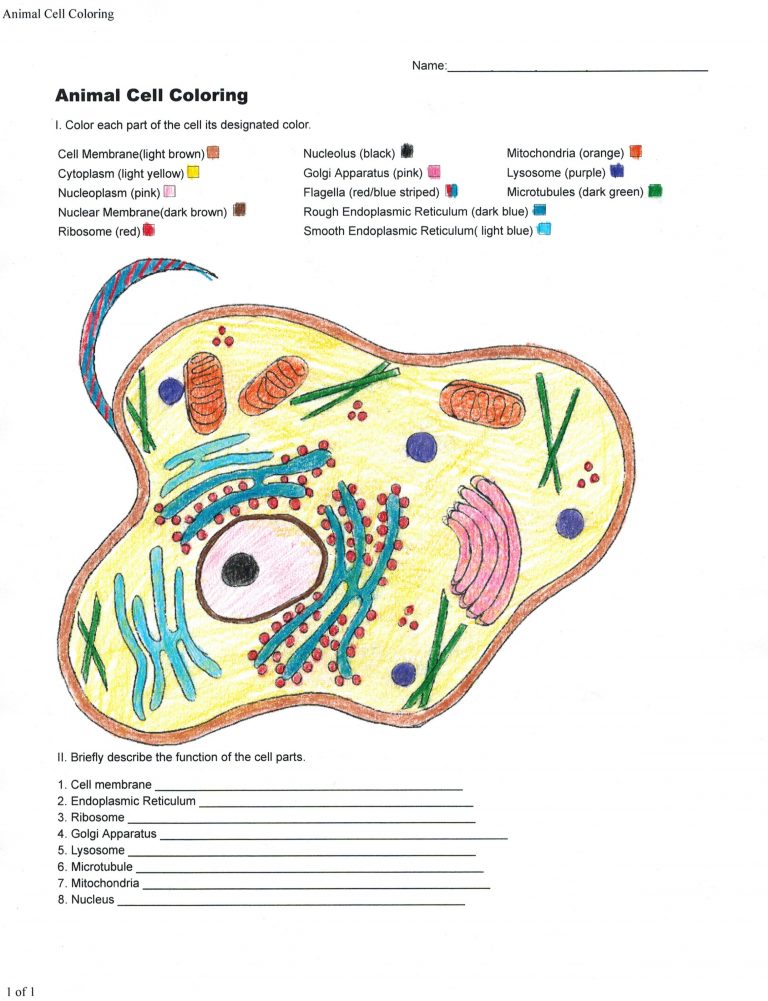
The microscopic world of animal cells is not only fascinating but also surprisingly vibrant. From the rich hues of organelles to the subtle shades of cellular structures, animal cell colors offer a unique insight into their function and diversity. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about the natural world, understanding these colors can deepen your appreciation for the complexity of life. In this guide, we'll explore the reasons behind these colors, their significance, and how they can be observed, all while keeping SEO in mind to ensure you find the information you need.
Why Do Animal Cells Have Colors?
Animal cells exhibit colors due to the presence of pigments, staining techniques, and natural biochemical processes. These colors are not just aesthetically pleasing but often indicate specific functions or states of the cell. For instance, mitochondria may appear red or yellow under certain stains, highlighting their role as the cell’s powerhouses. Understanding these colors can aid in scientific research, educational studies, and even medical diagnostics.
Common Colors in Animal Cells and Their Meanings
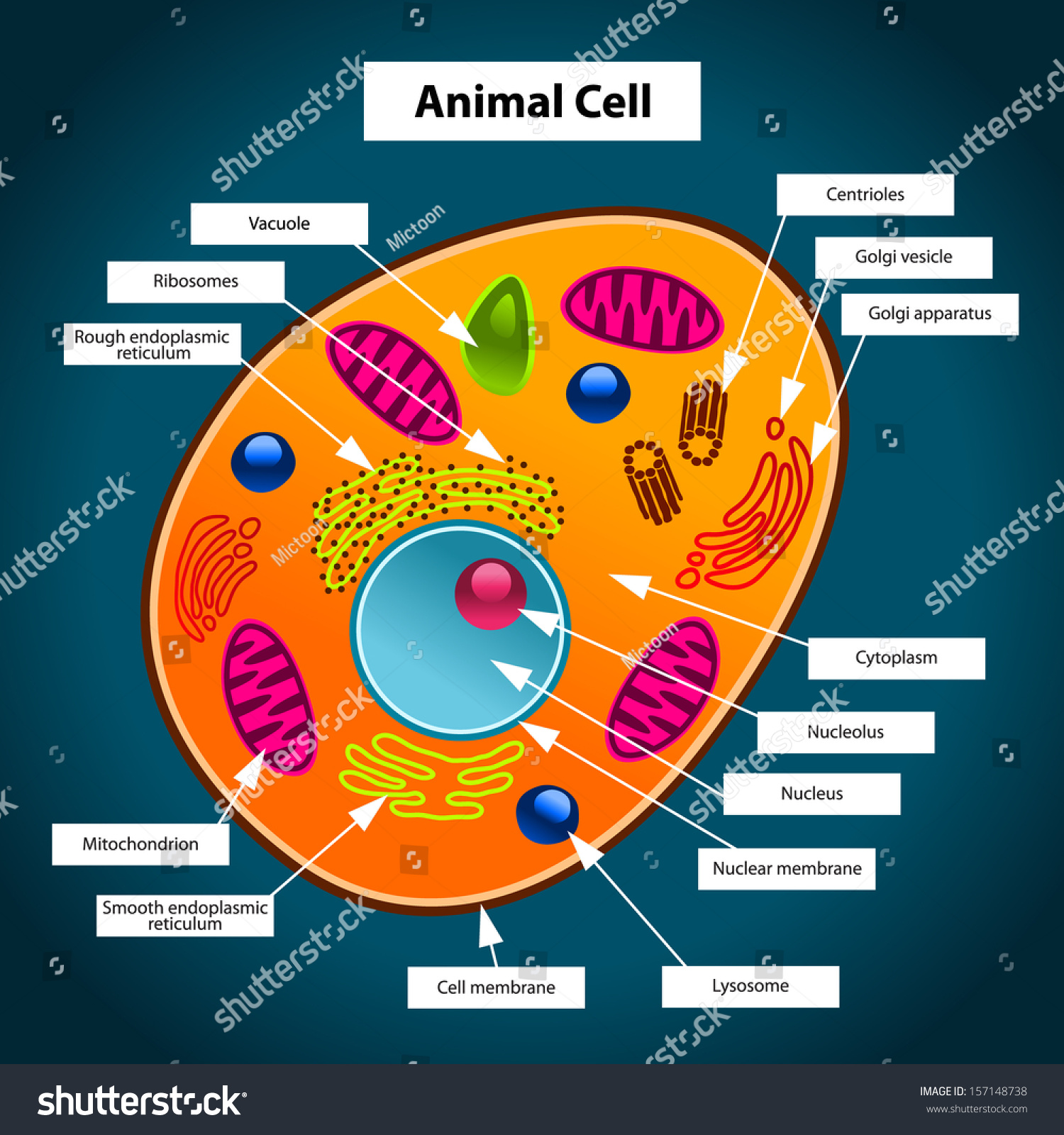
Different structures within animal cells can display a range of colors when stained or observed under a microscope. Here’s a breakdown of some common colors and what they signify:
- Blue/Purple: Often indicates the presence of DNA or RNA, typically stained with dyes like DAPI or Hoechst.
- Red/Pink: Commonly associated with cytoplasm or specific proteins, stained with dyes like Eosin.
- Green: Frequently used to highlight cell membranes or specific proteins, often with dyes like FITC.
- Yellow/Orange: May indicate the presence of lipids or certain organelles like mitochondria, stained with dyes like Nile Red.
| Stain | Color | Targets |
|---|---|---|
| DAPI | Blue | DNA |
| Eosin | Red/Pink | Cytoplasm, Proteins |
| FITC | Green | Cell Membrane, Proteins |
| Nile Red | Yellow/Orange | Lipids, Mitochondria |
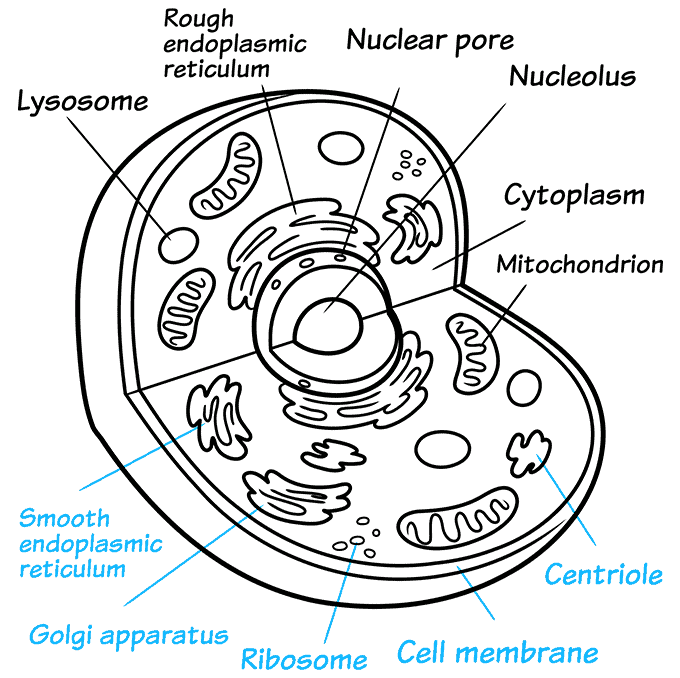
How to Observe Animal Cell Colors
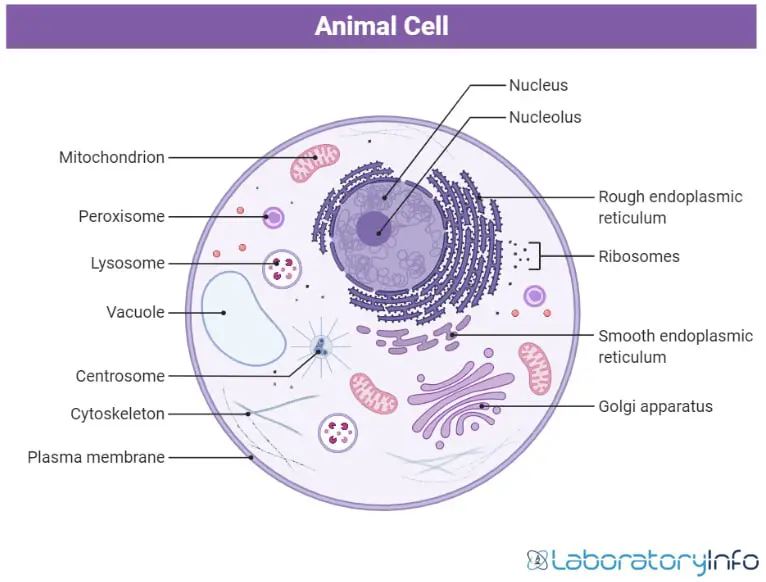
Observing the colors of animal cells requires specific techniques and tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Prepare the Sample: Fix and stain the cells using appropriate dyes.
- Use a Microscope: A compound light microscope or fluorescence microscope is ideal for observing stained cells.
- Adjust Lighting: Ensure proper illumination to enhance color visibility.
- Record Observations: Take notes or images for further analysis.
💡 Note: Always follow safety protocols when handling stains and chemicals in the lab.
Applications of Studying Animal Cell Colors
The study of animal cell colors has practical applications in various fields:
- Research: Understanding cellular processes and diseases.
- Education: Enhancing biology lessons with visual aids.
- Medicine: Diagnosing cellular abnormalities and developing treatments.
In summary, animal cell colors are a window into the intricate world of cellular biology. By understanding these colors and their significance, we can gain valuable insights into how cells function, interact, and respond to their environment. Whether for academic, professional, or personal interest, exploring animal cell colors is both enlightening and visually captivating. (animal cell structure, cell biology, microscopy techniques)
What causes animal cells to have different colors?
+Animal cells exhibit different colors due to pigments, staining techniques, and natural biochemical processes that highlight specific structures or functions.
Can animal cell colors indicate health issues?
+Yes, abnormal colors or patterns in animal cells can indicate health issues such as disease, damage, or dysfunction, making them valuable in diagnostics.
What tools are needed to observe animal cell colors?
+A compound light microscope or fluorescence microscope, along with appropriate stains, is essential for observing animal cell colors.



