Antimony: Unveiling the Secrets of Atomic Number 51

Antimony, a lesser-known yet fascinating element with atomic number 51, has been an essential part of human history and modern technology. From ancient civilizations to cutting-edge industries, this metalloid has left its mark. In this blog, we’ll explore antimony’s properties, applications, and significance, tailored for both informational and commercial audiences.
What is Antimony? Unlocking the Basics

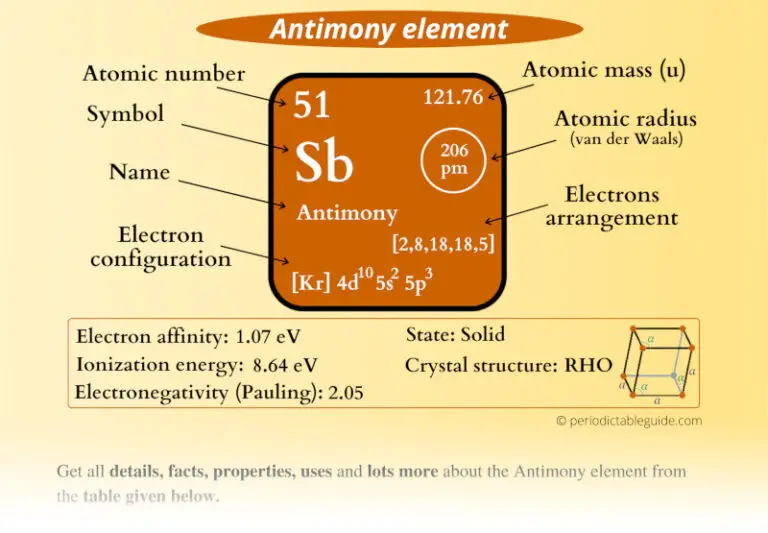
Antimony (Sb) is a lustrous gray metalloid found in nature primarily as stibnite (Sb₂S₃). It exists in two forms: metallic and non-metallic, making it versatile for various uses. With a melting point of 630.63°C, antimony is highly durable and resistant to corrosion, properties that make it invaluable in industries like electronics, alloys, and flame retardants.
💡 Note: Antimony is not found freely in nature and is usually extracted from its sulfide ores.
Historical Significance of Antimony

Antimony’s use dates back to ancient Egypt, where it was applied in cosmetics, particularly in kohl eyeliner. During the Middle Ages, it became a key component in alloys, enhancing the hardness of lead for printing type. Its historical applications highlight its enduring importance across cultures.
Modern Applications of Antimony

Today, antimony is a critical element in several industries:
1. Flame Retardants
Antimony trioxide (Sb₂O₃) is widely used in plastics, textiles, and electronics to inhibit the spread of flames. This application ensures safety in products like cables, toys, and building materials.
2. Alloys
Antimony alloys, such as lead-antimony batteries, are essential in energy storage systems. These alloys improve hardness and durability, making them ideal for automotive and industrial use.
3. Electronics
In the tech industry, antimony is used in semiconductor devices and infrared sensors. Its unique properties enable efficient heat dissipation and conductivity.
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Flame Retardants | Fire Safety |
| Alloys | Enhanced Durability |
| Electronics | Improved Conductivity |

Environmental and Health Considerations

While antimony is invaluable, its extraction and use pose environmental and health risks. Exposure to antimony compounds can cause respiratory issues and skin irritation. Proper handling and disposal are crucial to mitigate these risks.
⚠️ Note: Always follow safety guidelines when working with antimony-based products.
Where to Buy Antimony Products
For commercial buyers, antimony compounds and alloys are available from specialized suppliers. Ensure you choose reputable vendors who comply with safety and environmental standards.
Key Takeaways
- Antimony is a versatile metalloid with applications in flame retardants, alloys, and electronics.
- Its historical significance spans from ancient cosmetics to modern technology.
- Safety and environmental considerations are essential when handling antimony.
What is antimony used for?
+Antimony is used in flame retardants, alloys, electronics, and historically in cosmetics.
Is antimony safe to handle?
+While antimony is essential in many products, exposure to its compounds can pose health risks. Always follow safety guidelines.
Where can I buy antimony products?
+Antimony compounds and alloys are available from specialized industrial suppliers.
Antimony’s journey from ancient times to modern technology showcases its indispensable role. Whether you’re an enthusiast or a buyer, understanding its properties and applications can help you appreciate its value.
antimony properties,antimony uses,antimony alloys,flame retardants,electronics materials,industrial chemicals