Decoding Blood Agar Results: A Quick Guide Blood Agar Results Explained: Key Insights Understanding Blood Agar Results: What to Look For How to Interpret Blood Agar Results Effectively Blood Agar Results: Essential Tips for Analysis
Blood agar is a cornerstone in microbiology, widely used for isolating and identifying bacteria. Its ability to differentiate between bacterial species based on their hemolytic activity makes it an essential tool in clinical and research settings. Whether you're a student, lab technician, or researcher, understanding how to interpret blood agar results is crucial. This guide will walk you through the key insights, essential tips, and effective analysis techniques to decode blood agar results with confidence.
Understanding Blood Agar Results: What to Look For
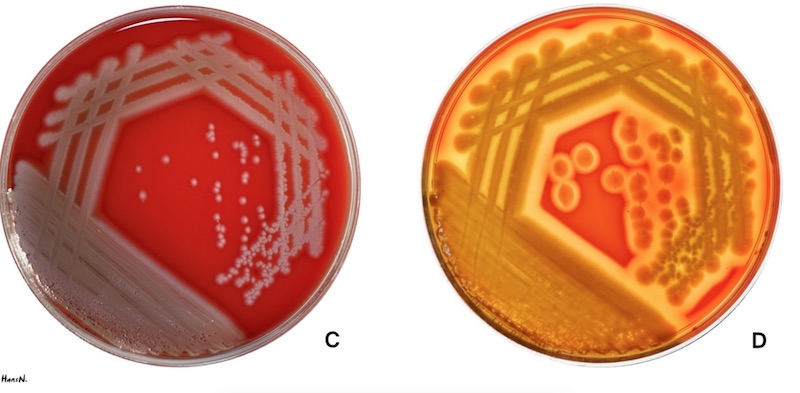
Blood agar plates contain sheep, horse, or rabbit blood, which allows for the detection of hemolytic activity. Bacteria interact with the blood in different ways, producing distinct zones around the colonies. Here’s what to focus on:
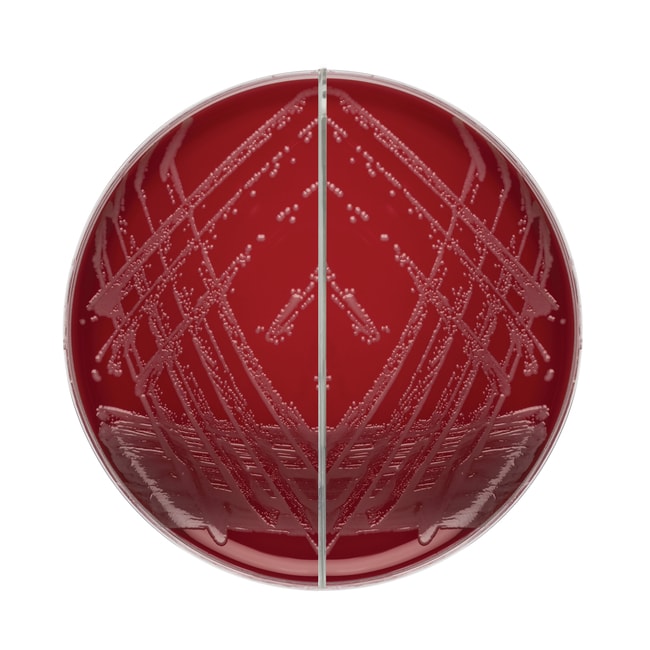
- Alpha-hemolysis: Partial lysis of red blood cells, appearing as a green or brown discoloration around the colony.
- Beta-hemolysis: Complete lysis of red blood cells, resulting in a clear zone around the colony.
- Gamma-hemolysis: No hemolysis, with no visible change in the blood agar.
Identifying these patterns is the first step in classifying bacterial isolates. (blood agar results, hemolysis types, bacterial identification)
How to Interpret Blood Agar Results Effectively

Interpreting blood agar results requires attention to detail and an understanding of bacterial behavior. Follow these steps for accurate analysis:
- Inspect Colony Morphology: Note the size, shape, color, and texture of the colonies.
- Assess Hemolytic Zones: Determine the type of hemolysis (alpha, beta, or gamma) based on the appearance of the agar.
- Compare with Known Standards: Use reference charts or databases to match your findings with known bacterial species.
📌 Note: Always incubate plates at the correct temperature (typically 37°C) for 24–48 hours to ensure accurate results.
Blood Agar Results: Essential Tips for Analysis

To streamline your analysis, keep these tips in mind:
- Use Fresh Plates: Ensure blood agar plates are fresh and stored properly to avoid false results.
- Control Contamination: Work in a sterile environment to prevent contamination that could skew results.
- Document Observations: Record detailed notes on colony characteristics and hemolytic patterns for future reference.
These practices will enhance the reliability of your blood agar results. (blood agar analysis, lab techniques, contamination prevention)
Checklist for Decoding Blood Agar Results

Use this checklist to ensure thorough analysis:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Inspect colony morphology (size, shape, color, texture) |
| 2 | Identify hemolysis type (alpha, beta, gamma) |
| 3 | Compare results with known bacterial standards |
| 4 | Document observations and findings |
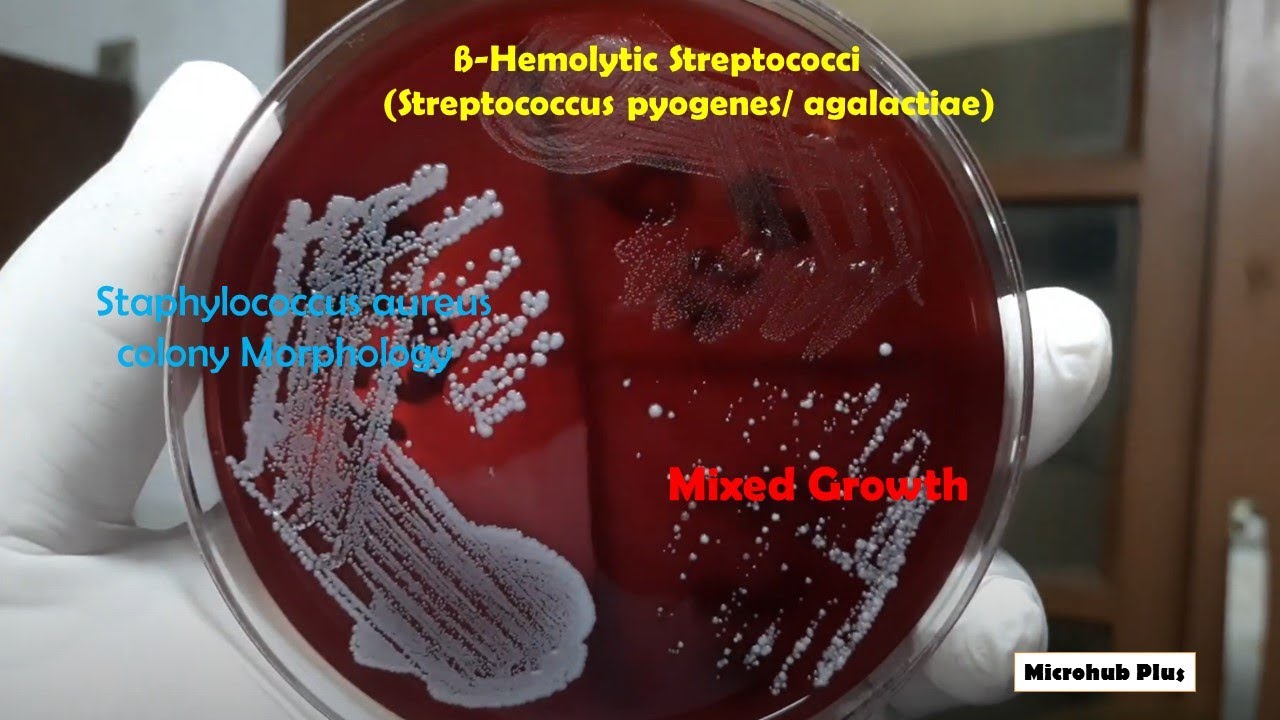
Decoding blood agar results is a skill that improves with practice and attention to detail. By focusing on colony morphology, hemolytic patterns, and proper lab techniques, you can confidently identify bacterial species and contribute to accurate diagnoses or research findings. Remember, consistency and precision are key to mastering blood agar analysis. (blood agar results explained, microbiology techniques, lab skills)
What does beta-hemolysis indicate on blood agar?
+
Beta-hemolysis indicates complete lysis of red blood cells, resulting in a clear zone around the bacterial colony. This is often associated with pathogens like Streptococcus pyogenes.
Can gamma-hemolysis be used to identify bacteria?
+
Gamma-hemolysis (no hemolysis) alone is not sufficient for identification but is a characteristic to note. It is often seen in bacteria like Enterococcus species.
How long should blood agar plates be incubated?
+
Blood agar plates should be incubated at 37°C for 24–48 hours to allow sufficient bacterial growth and hemolytic activity.



