Forest Consumers: Survival Strategies in Nature's Web
Forests are bustling ecosystems where every organism plays a role in the intricate web of life. Among these, forest consumers are vital for maintaining balance and ensuring the survival of the entire ecosystem. From herbivores to omnivores, these creatures rely on unique strategies to thrive in their natural habitats. Understanding their survival techniques not only sheds light on their adaptability but also highlights the importance of preserving these environments. Whether you're an eco-enthusiast or a nature lover, exploring the world of forest consumers offers valuable insights into the delicate dynamics of nature's web,forest ecosystem,wildlife survival,biodiversity.
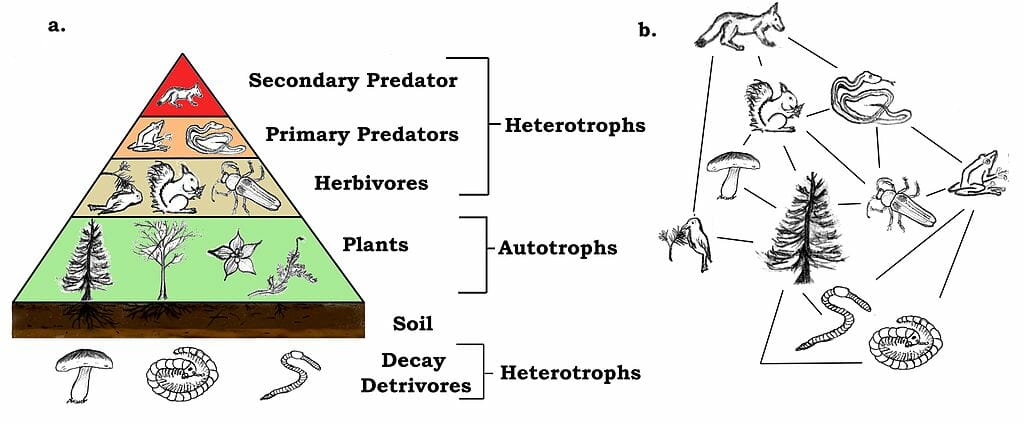
Understanding Forest Consumers: Roles and Importance

Forest consumers are organisms that rely on other living beings for sustenance. They include herbivores, omnivores, and even some carnivores that feed on smaller animals. These consumers play a critical role in nutrient cycling, seed dispersal, and controlling plant populations. Without them, forests would face imbalances, such as overgrowth or the decline of certain plant species. Their survival strategies are as diverse as the forests they inhabit, ranging from camouflage to migration,forest biodiversity,ecological balance,consumer species.
Key Survival Strategies of Forest Consumers
1. Camouflage and Concealment
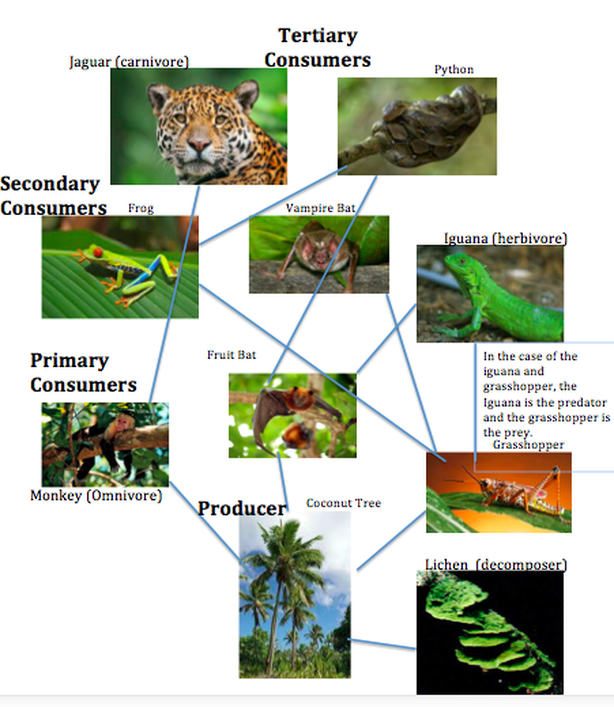
Many forest consumers, like the stick insect or snowshoe hare, use camouflage to blend into their surroundings. This strategy helps them avoid predators while hunting or foraging. For example, the snowshoe hare changes its fur color with the seasons, ensuring it remains hidden year-round. Concealment is equally vital for predators like owls, which rely on stealth to catch their prey,predator avoidance,adaptive coloration,survival tactics.
2. Migration and Movement
Some forest consumers, such as deer and birds, employ migration to access food and shelter during harsh seasons. Migration allows them to follow resource availability, ensuring their survival in changing environments. Even smaller creatures, like certain insect species, migrate in search of favorable conditions. This strategy not only aids individual survival but also supports the health of the entire forest ecosystem,seasonal adaptation,animal migration,resource utilization.
3. Cooperative Behavior
Cooperation is another survival strategy seen in species like wolves and bees. Wolves hunt in packs, increasing their chances of success, while bees work together to maintain their hive. Such behaviors enhance their ability to secure food and protect themselves from predators. Cooperative behavior is a testament to the strength of unity in nature’s web,social animals,group dynamics,community survival.
How Humans Can Support Forest Consumers

As stewards of the planet, humans play a crucial role in protecting forest consumers and their habitats. Here are actionable steps to make a difference:
- Preserve Habitats: Support reforestation and conservation efforts to maintain natural habitats.
- Reduce Pollution: Minimize the use of harmful chemicals that can disrupt ecosystems.
- Promote Biodiversity: Encourage the growth of diverse plant species to support various consumers.
- Educate Others: Raise awareness about the importance of forest consumers in ecological balance.
🌿 Note: Small actions, like planting native trees or reducing waste, can significantly impact forest ecosystems,conservation efforts,environmental protection,sustainable practices.
| Survival Strategy | Example Species | Benefit to Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|
| Camouflage | Snowshoe Hare | Maintains predator-prey balance |
| Migration | Monarch Butterfly | Supports pollination and seed dispersal |
| Cooperation | African Wild Dogs | Enhances hunting efficiency and species survival |
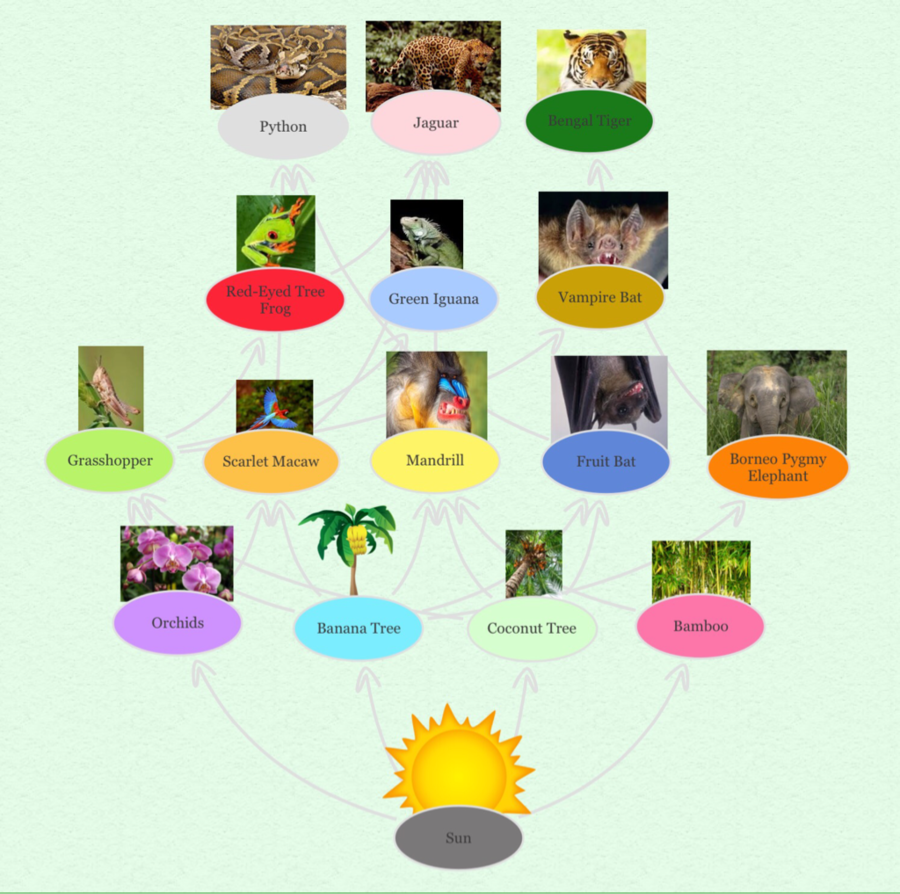
Checklist for Supporting Forest Consumers
- Plant native trees and shrubs in your area.
- Avoid using pesticides and herbicides in your garden.
- Participate in local conservation programs or initiatives.
- Educate your community about the importance of forest biodiversity.
Forest consumers are the unsung heroes of ecosystems, employing remarkable strategies to survive and thrive. By understanding their roles and supporting their habitats, we contribute to the health of our planet. Whether through conservation efforts or simple daily actions, every step counts in preserving nature's delicate web,ecosystem preservation,wildlife conservation,environmental stewardship.
What are forest consumers?
+
Forest consumers are organisms that rely on other living beings for food, including herbivores, omnivores, and carnivores,forest ecosystem,consumer species.
Why are forest consumers important?
+
They maintain ecological balance by controlling plant populations, aiding in nutrient cycling, and supporting biodiversity,ecological balance,biodiversity.
How can I help protect forest consumers?
+
Support conservation efforts, reduce pollution, and promote habitat preservation through reforestation and sustainable practices,conservation efforts,sustainable living.



