Examples of Integral Proteins: Key Membrane Components Explained

Integral proteins are essential components of biological membranes, playing critical roles in cell function, communication, and transport. These proteins are permanently embedded within the lipid bilayer, distinguishing them from peripheral proteins that attach temporarily. Understanding integral proteins is key to grasping how cells interact with their environment and maintain internal balance. This post explores examples of integral proteins, their functions, and their significance in biology and biotechnology.
What Are Integral Proteins?
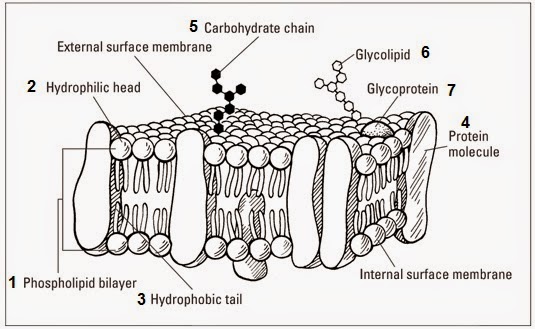
Integral proteins, also known as intrinsic proteins, are membrane-spanning proteins that penetrate the entire lipid bilayer. They are classified into two main types: transmembrane proteins and integral monotopic proteins. Transmembrane proteins span the entire membrane, while monotopic proteins are attached to only one side of the lipid bilayer.
💡 Note: Integral proteins are crucial for cellular processes like signal transduction, nutrient transport, and cell adhesion.
Examples of Integral Proteins

1. Ion Channels
Ion channels are integral proteins that regulate the flow of ions (e.g., sodium, potassium, calcium) across the cell membrane. They are vital for nerve impulses, muscle contractions, and maintaining cellular pH.
- Example: Voltage-gated sodium channels enable the rapid transmission of electrical signals in neurons.
2. Aquaporins
Aquaporins are integral proteins that facilitate the movement of water molecules across cell membranes. They are essential for hydration, osmoregulation, and nutrient transport.
- Example: AQP1 (Aquaporin 1) is found in red blood cells and kidney tubules, ensuring efficient water transport.
3. G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
GPCRs are integral proteins involved in signal transduction, responding to extracellular signals like hormones and neurotransmitters.
- Example: Beta-adrenergic receptors bind adrenaline, triggering cellular responses like increased heart rate.
| Protein Type | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Ion Channels | Ion transport | Voltage-gated sodium channels |
| Aquaporins | Water transport | AQP1 |
| GPCRs | Signal transduction | Beta-adrenergic receptors |

Commercial Applications of Integral Proteins
Integral proteins are not only fundamental in biology but also have significant commercial applications. They are targeted in drug development, biotechnology, and medical research.
- Pharmaceuticals: Drugs like beta-blockers target GPCRs to treat hypertension and heart disease.
- Biotechnology: Aquaporins are used in water filtration systems for efficient desalination.
💊 Note: The global market for GPCR-targeted drugs is projected to grow significantly due to their role in treating various diseases.
Key Takeaways

- Integral proteins are permanently embedded in cell membranes and are essential for transport, signaling, and cell structure.
- Examples include ion channels, aquaporins, and GPCRs, each with unique functions.
- These proteins have wide-ranging applications in medicine and biotechnology, making them a focus of ongoing research.
Checklist for Understanding Integral Proteins:
- Identify the types of integral proteins (transmembrane, monotopic).
- Recognize their roles in ion transport, water movement, and signal transduction.
- Explore their commercial applications in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
What is the primary function of integral proteins?
+Integral proteins primarily facilitate transport, signaling, and structural support within cell membranes.
How do ion channels differ from aquaporins?
+Ion channels transport ions like sodium and potassium, while aquaporins specifically transport water molecules.
Why are GPCRs important in drug development?
+GPCRs are targeted in drug development because they play a key role in cellular signaling pathways, making them ideal for treating diseases like hypertension and diabetes.
In summary, integral proteins are indispensable for cellular function and have transformative applications in science and industry. By understanding their roles and examples, we gain insights into their importance in biology and beyond,membrane biology,protein function,cell signaling,biotechnology advancements,pharmaceutical research.