Federalist vs Anti-Federalist: Key Differences Explained

The debate between Federalists and Anti-Federalists is a cornerstone of American political history, shaping the foundations of the United States Constitution. Understanding their differences is crucial for anyone interested in the early political philosophies that still influence modern governance. This post explores the key distinctions between these two groups, their beliefs, and their impact on the Constitution, tailored for both informational and commercial audiences.
What Were the Federalist and Anti-Federalist Movements?

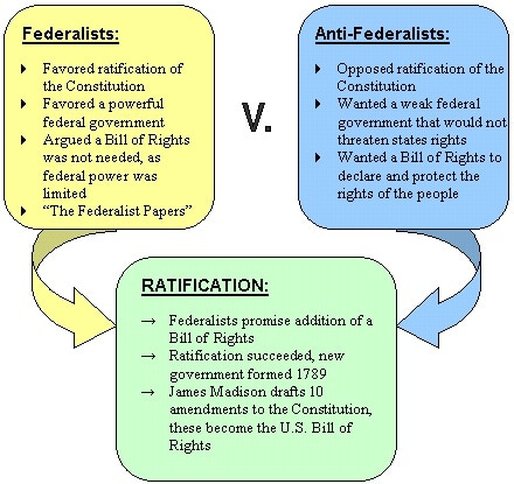
The Federalists and Anti-Federalists were two factions that emerged during the ratification of the U.S. Constitution in the late 18th century. Their clash centered on the structure and power of the federal government, with each side advocating for vastly different visions of governance.
Federalists: Advocates for a Strong Central Government
Federalists, led by figures like Alexander Hamilton and James Madison, supported the ratification of the Constitution. They believed in a strong central government to ensure stability, economic growth, and national unity. Key Federalist beliefs included:
- Centralized Authority: A powerful federal government to maintain order and prevent state conflicts.
- Economic Prosperity: Uniform policies to promote trade and commerce.
- Checks and Balances: A system to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
💡 Note: Federalists were instrumental in the creation of the Federalist Papers, which remain a primary source for understanding their arguments.
Anti-Federalists: Champions of States’ Rights
Anti-Federalists, including Patrick Henry and George Mason, opposed the Constitution, fearing it would undermine individual liberties and state sovereignty. Their core beliefs were:
- States’ Rights: Strong state governments to protect local interests and autonomy.
- Limited Federal Power: A central government with minimal authority to prevent tyranny.
- Bill of Rights: A demand for explicit protections of individual freedoms.
Key Differences Between Federalists and Anti-Federalists

To better understand their contrasting views, here’s a comparison table:
| Aspect | Federalists | Anti-Federalists |
|---|---|---|
| Central Government | Strong and centralized | Weak and limited |
| States' Rights | Secondary to federal authority | Primary focus |
| Constitution View | Supported ratification | Opposed without a Bill of Rights |

Impact on the Constitution
The debate between Federalists and Anti-Federalists led to significant compromises, most notably the addition of the Bill of Rights. This ensured individual liberties, addressing Anti-Federalist concerns while maintaining the Federalist vision of a strong central government.
Federalist vs Anti-Federalist: A Checklist of Differences

- Government Structure: Federalists favored a strong central government; Anti-Federalists prioritized states’ rights.
- Economic Policies: Federalists supported national economic policies; Anti-Federalists preferred local control.
- Individual Liberties: Anti-Federalists pushed for explicit protections; Federalists believed checks and balances were sufficient.
Why Does This Matter Today?
The Federalist vs Anti-Federalist debate continues to influence modern political discourse, particularly in discussions about federal vs. state authority, individual rights, and the role of government. Understanding these historical perspectives provides valuable insights into contemporary political challenges.
What was the main goal of the Federalists?
+Federalists aimed to establish a strong central government to ensure national stability and economic growth.
Why did Anti-Federalists oppose the Constitution?
+Anti-Federalists feared a strong central government would threaten individual liberties and state sovereignty.
How did the Federalist-Anti-Federalist debate shape the Constitution?
+The debate led to the addition of the Bill of Rights, balancing federal power with individual protections.
The Federalist and Anti-Federalist debate remains a critical chapter in American history, offering lessons on governance, liberty, and compromise. By understanding their differences, we gain insights into the enduring principles that shape our political system today. (Federalist vs Anti-Federalist, U.S. Constitution, American History)



