Maximizing Oxygen Delivery: Non-Rebreather Mask Flow Rate Guide
<!DOCTYPE html>
Delivering the right amount of oxygen to patients in need is critical in medical emergencies. A non-rebreather mask is a vital tool for this purpose, but understanding the correct flow rate is essential for maximizing its effectiveness. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about non-rebreather mask flow rates, ensuring optimal oxygen delivery for your patients. (oxygen therapy, non-rebreather mask, emergency medical care)
Understanding Non-Rebreather Masks and Flow Rates

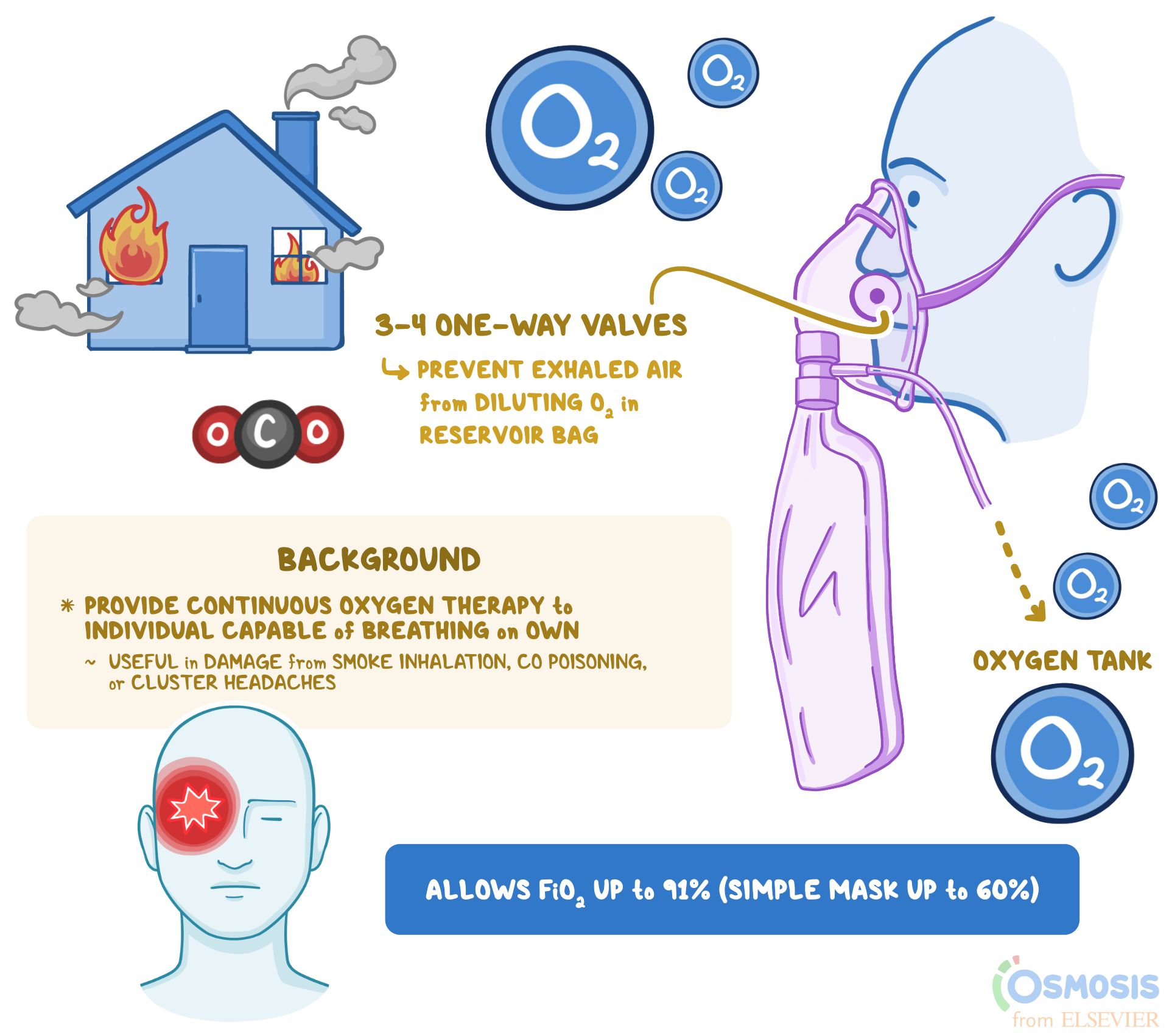
Non-rebreather masks are designed to deliver high concentrations of oxygen to patients who require it. Unlike simple face masks, they feature a one-way valve system that prevents the inhalation of room air, ensuring the patient receives nearly 100% oxygen. The flow rate, measured in liters per minute (L/min), determines how much oxygen is delivered.
Factors Influencing Flow Rate Selection
Several factors influence the appropriate flow rate for a non-rebreather mask:
- Patient’s Oxygen Needs: Determined by their condition and oxygen saturation levels.
- Mask Fit: A proper seal ensures efficient oxygen delivery.
- Reservoir Bag Size: Larger bags can hold more oxygen, allowing for lower flow rates.
Optimal Flow Rate Guidelines

While specific needs vary, general guidelines suggest starting with a flow rate of 10-15 L/min for adults. This ensures the reservoir bag remains inflated, providing a continuous supply of oxygen. For children, flow rates are typically lower, ranging from 6-8 L/min, depending on their size and condition.
| Patient Age | Recommended Flow Rate (L/min) |
|---|---|
| Adults | 10-15 |
| Children | 6-8 |

💡 Note: Always monitor the patient’s oxygen saturation levels and adjust the flow rate as needed to maintain adequate oxygenation.
Steps to Ensure Proper Oxygen Delivery

- Assess the Patient: Evaluate their oxygen needs based on their condition and current saturation levels.
- Select the Right Mask: Ensure the mask fits properly to create a tight seal.
- Set the Flow Rate: Start with the recommended rate and adjust based on the patient’s response.
- Monitor Continuously: Regularly check oxygen saturation and adjust settings as necessary.
Checklist for Optimal Oxygen Delivery
- Verify the mask is properly sealed.
- Ensure the reservoir bag remains inflated.
- Monitor oxygen saturation levels regularly.
- Adjust flow rate as needed to maintain adequate oxygenation.
Mastering the use of a non-rebreather mask and understanding the correct flow rate are crucial for effective oxygen therapy. By following these guidelines, healthcare providers can ensure patients receive the oxygen they need in critical situations. (oxygen therapy, non-rebreather mask, emergency medical care)
What is the purpose of a non-rebreather mask?
+A non-rebreather mask is designed to deliver high concentrations of oxygen to patients by preventing the inhalation of room air, ensuring they receive nearly 100% oxygen.
How do I know if the non-rebreather mask is working properly?
+Ensure the reservoir bag remains inflated and the mask is properly sealed. Monitor the patient’s oxygen saturation levels to confirm adequate oxygenation.
Can I use a non-rebreather mask for children?
+Yes, but use a lower flow rate (6-8 L/min) and ensure the mask fits properly to avoid leaks.



