Understanding the Formula of Charge Density: A Quick Guide
<!DOCTYPE html>
Charge density is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, representing the amount of electric charge distributed over a given area, volume, or length. Understanding its formula is crucial for applications in electromagnetism, electronics, and material science. This guide breaks down the concept, formula, and practical applications of charge density, ensuring you grasp it quickly and effectively. (charge density formula, electric charge distribution, physics concepts)
What is Charge Density?

Charge density measures how electric charge is spread across a specific region. It is classified into three types based on the dimensionality of the region:
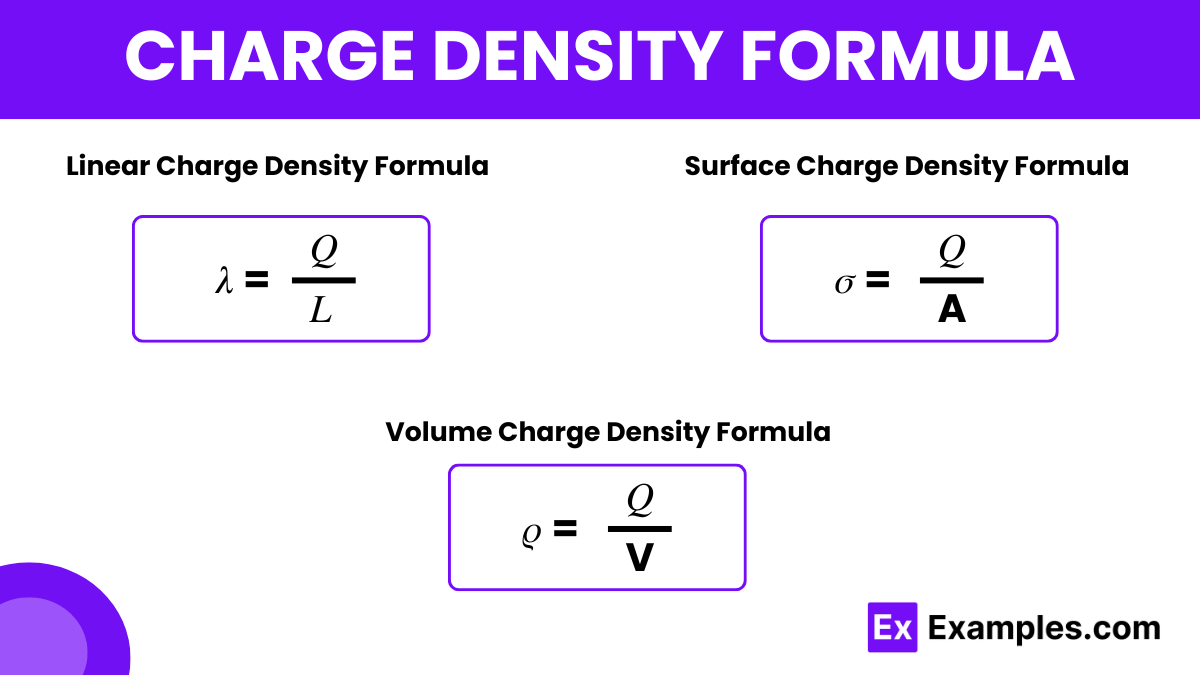
- Linear Charge Density (λ): Charge per unit length, often used in wires or linear conductors.
- Surface Charge Density (σ): Charge per unit area, applicable to flat surfaces or plates.
- Volume Charge Density (ρ): Charge per unit volume, used for three-dimensional objects.
Each type has its unique formula, tailored to the geometry of the charged object. (linear charge density, surface charge density, volume charge density)
The Formula of Charge Density

The formula for charge density depends on its type. Below are the key formulas:
| Type | Formula | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Charge Density (λ) | λ = Q / L | C/m |
| Surface Charge Density (σ) | σ = Q / A | C/m² |
| Volume Charge Density (ρ) | ρ = Q / V | C/m³ |

Where: Q = Total charge, L = Length, A = Area, V = Volume. (charge density calculation, charge density units, physics formulas)
How to Calculate Charge Density

Calculating charge density involves these steps:
- Identify the type of charge density based on the object’s geometry.
- Measure the total charge (Q) in coulombs ©.
- Determine the appropriate dimension (length, area, or volume).
- Apply the corresponding formula to find the charge density.
📌 Note: Ensure consistent units for accurate calculations. (charge density steps, charge density measurement, physics tutorials)
Practical Applications of Charge Density

Charge density is vital in various fields:
- Electronics: Designing capacitors and conductors.
- Material Science: Analyzing dielectric materials.
- Electromagnetism: Studying electric fields and forces.
Understanding charge density enhances efficiency and innovation in these areas. (charge density applications, electronics engineering, material science)
Checklist for Mastering Charge Density

- Learn the three types of charge density.
- Memorize the formulas for each type.
- Practice calculating charge density with real-world examples.
- Explore applications in your field of interest.
This checklist ensures a solid foundation in charge density concepts. (charge density checklist, physics learning, engineering tips)
What is the unit of volume charge density?
+The unit of volume charge density (ρ) is coulombs per cubic meter (C/m³).
How does charge density affect electric fields?
+Higher charge density creates stronger electric fields, influencing force and potential differences.
Can charge density be negative?
+Yes, negative charge density indicates the presence of excess negative charge in the region.
In summary, charge density is a critical concept with straightforward formulas tailored to linear, surface, and volume distributions. By mastering these formulas and their applications, you can tackle complex problems in physics and engineering with confidence. Whether you're a student or a professional, this quick guide equips you with the knowledge to apply charge density effectively. (charge density summary, physics fundamentals, engineering knowledge)



