H2Te Boiling Point: Essential Facts & Insights
Hydrogen telluride (H2Te) is a colorless, highly toxic gas with a distinct garlic-like odor. Understanding its boiling point is crucial for applications in chemical research, industrial processes, and safety protocols. This post explores the H2Te boiling point, its significance, and essential facts to help both informational and commercial audiences grasp its importance.
What is the Boiling Point of H2Te?

The boiling point of H2Te is approximately -2.2°C (28.0°F). This low boiling point makes it a volatile compound, readily transitioning from a liquid to a gas under standard conditions. Its volatility is a key factor in handling and storage, especially in industrial settings.
💡 Note: Always ensure proper ventilation when working with H2Te due to its toxicity and volatility.
Factors Influencing H2Te Boiling Point

Several factors affect the boiling point of H2Te, including:
- Molecular Weight: H2Te has a relatively low molecular weight, contributing to its low boiling point.
- Intermolecular Forces: Weak van der Waals forces between molecules result in less energy required for phase transition.
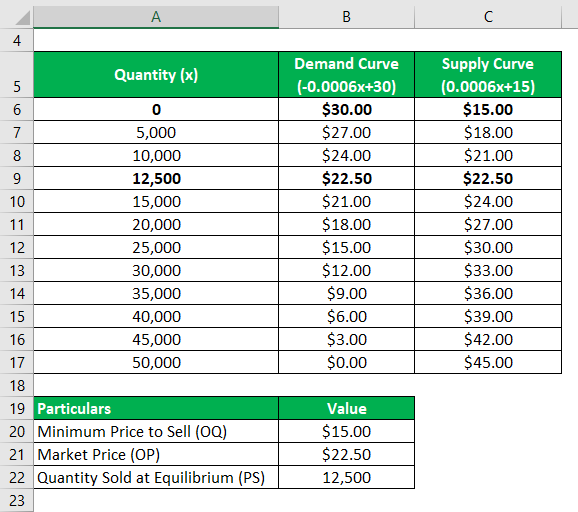
- Pressure: Changes in pressure can alter the boiling point, as per the Clausius-Clapeyron equation.
Understanding these factors is essential for precise control in chemical reactions and industrial applications. (H2Te properties, chemical compounds, industrial chemicals)
Applications of H2Te and Its Boiling Point

H2Te’s boiling point plays a critical role in its applications, including:
- Chemical Synthesis: Used in the production of tellurium compounds and semiconductors.
- Laboratory Research: A reagent in organic and inorganic chemistry experiments.
- Industrial Processes: Involved in the manufacturing of electronic materials and solar panels.
Its low boiling point ensures efficient handling and processing in these applications. (Chemical synthesis, industrial applications, laboratory research)
Safety Considerations for H2Te Handling

Due to its toxicity and volatility, handling H2Te requires strict safety measures:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use gloves, goggles, and respirators to minimize exposure.
- Ventilation: Work in fume hoods or well-ventilated areas to prevent inhalation.
- Storage: Store in airtight containers at low temperatures to prevent accidental release.
⚠️ Note: H2Te exposure can cause severe health issues, including respiratory failure and neurological damage.
(Chemical safety, hazardous materials, industrial safety)
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | -2.2°C (28.0°F) |
| Molecular Weight | 130.02 g/mol |
| Density (Gas) | 5.08 g/L |

Checklist for Safe Handling of H2Te
- Ensure proper ventilation in the workspace.
- Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves and respirators.
- Store H2Te in airtight containers at low temperatures.
- Train personnel on emergency response procedures.
The boiling point of H2Te is a critical property that influences its applications and handling requirements. By understanding its characteristics and safety measures, professionals can effectively utilize this compound in various industries. Whether for research, manufacturing, or safety protocols, knowledge of H2Te’s boiling point is indispensable. (Chemical properties, industrial chemicals, safety protocols)
What is the boiling point of H2Te?
+
The boiling point of H2Te is approximately -2.2°C (28.0°F).
Why is H2Te’s boiling point important?
+
Its low boiling point makes it volatile, affecting its handling, storage, and applications in chemical processes.
How should H2Te be stored safely?
+
Store H2Te in airtight containers at low temperatures, away from heat sources and open flames.