Hydrogen: A Nonmetal Element Explained
Hydrogen, the first element on the periodic table, is a nonmetal that plays a crucial role in science, industry, and the future of clean energy. Despite its simplicity—consisting of just one proton and one electron—hydrogen’s unique properties make it a versatile and essential element. From powering fuel cells to forming the basis of water, hydrogen’s applications are vast and impactful. This post explores its characteristics, uses, and potential as a sustainable energy source, catering to both informational and commercial interests. (hydrogen properties, hydrogen uses, clean energy)
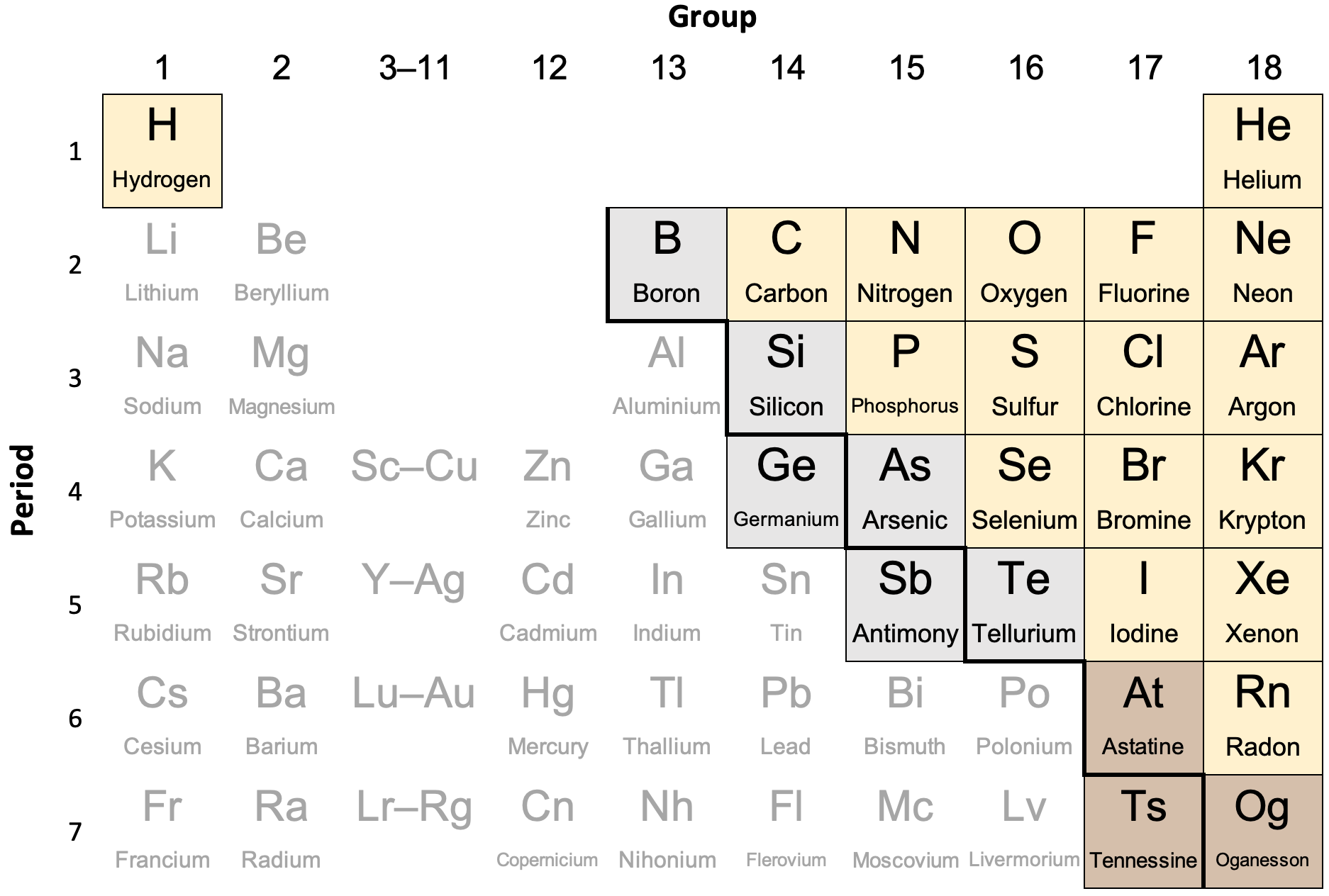
What is Hydrogen? A Nonmetal Element Overview
Hydrogen (H) is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe. Classified as a nonmetal, it exists primarily as a diatomic gas (H₂) under standard conditions. Its position at the top of the periodic table reflects its simplicity and uniqueness. Hydrogen’s ability to form bonds with nearly every element makes it a key player in chemistry and industry. (periodic table, diatomic gas, chemical bonding)
Key Properties of Hydrogen
Understanding hydrogen’s properties is essential to grasp its potential. Here are its notable characteristics:
- Lightweight: The lightest element, making it ideal for applications like balloons and aerospace.
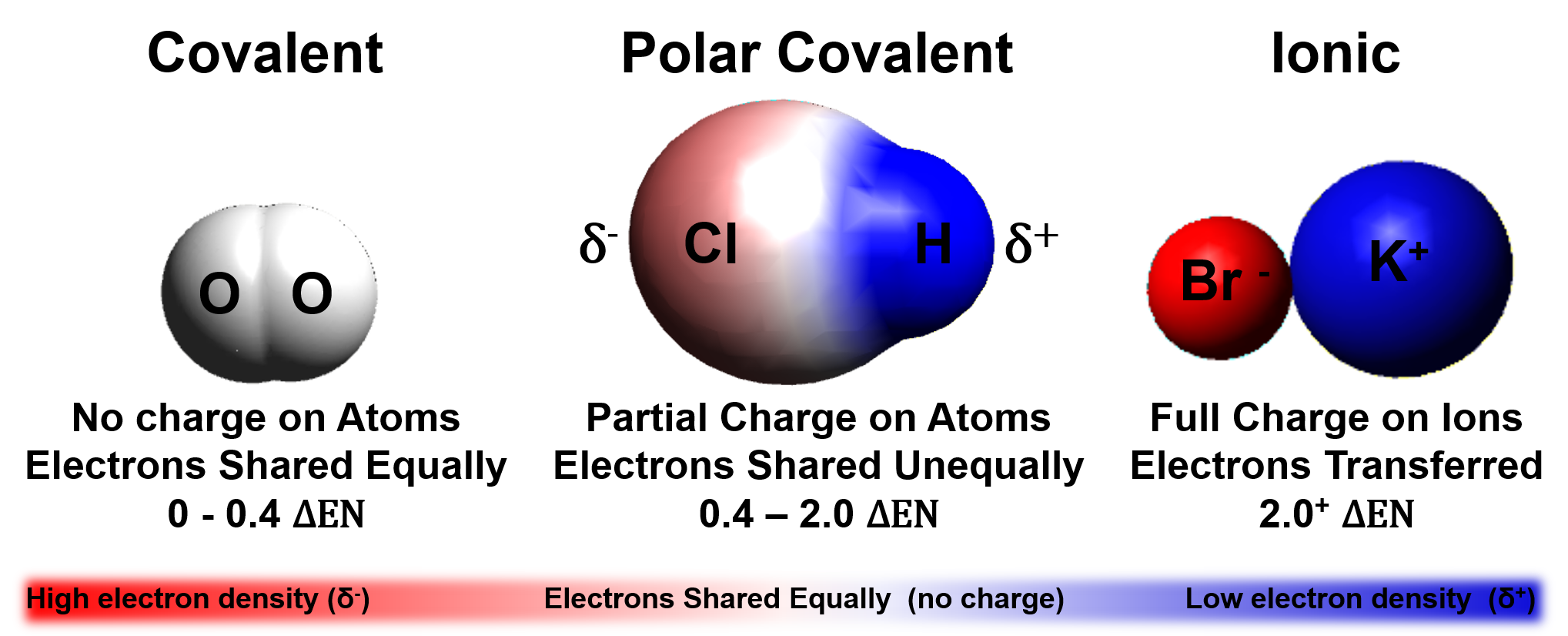
- Highly Reactive: Easily forms compounds with other elements, such as water (H₂O) and methane (CH₄).
- Flammable: Burns cleanly with oxygen, producing only water vapor, making it a clean fuel source.
- Colorless and Odorless: Exists as a gas in its natural state, undetectable without specialized tools.
(hydrogen properties, clean fuel, chemical reactions)
Hydrogen’s Role in Industry and Energy
Industrial Applications
Hydrogen is widely used in industries such as:
- Ammonia Production: Essential for fertilizers, ensuring global food security.
- Petroleum Refining: Used to remove impurities from crude oil, improving fuel quality.
- Metal Processing: Reduces metal oxides to pure metals, crucial for manufacturing.
(ammonia production, petroleum refining, metal processing)
Hydrogen as a Clean Energy Source
Hydrogen’s potential as a sustainable energy solution is gaining momentum. When used in fuel cells, it generates electricity with water as the only byproduct. This makes it a promising alternative to fossil fuels, especially for transportation and power generation. (sustainable energy, fuel cells, clean energy)
| Method | Description | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Steam Methane Reforming | Most common method, uses natural gas. | High CO₂ emissions. |
| Electrolysis | Splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. | Low emissions if renewable energy is used. |
| Biomass Gasification | Converts organic materials into hydrogen. | Moderate emissions, depends on feedstock. |

(hydrogen production, electrolysis, renewable energy)
💡 Note: Electrolysis is the most sustainable method for hydrogen production when powered by renewable energy sources.
Summary: Hydrogen’s Potential and Applications

Hydrogen’s unique properties and versatility make it a cornerstone of modern science and industry. From its role in chemical processes to its promise as a clean energy source, hydrogen is poised to shape a sustainable future. Whether you’re exploring its scientific significance or its commercial applications, hydrogen offers endless possibilities. (hydrogen potential, sustainable future, commercial applications)
Checklist for Hydrogen Utilization
- Evaluate the most suitable hydrogen production method for your needs.
- Consider fuel cells for clean energy solutions in transportation or power generation.
- Explore industrial applications like ammonia production or metal processing.
- Invest in renewable energy to minimize the environmental impact of hydrogen production.
(hydrogen production, fuel cells, renewable energy)
Is hydrogen a metal or nonmetal?
+Hydrogen is classified as a nonmetal due to its properties, such as low density and poor electrical conductivity.
How is hydrogen used in clean energy?
+Hydrogen is used in fuel cells to generate electricity, producing only water as a byproduct, making it a clean energy source.
What are the main methods of hydrogen production?
+The primary methods include steam methane reforming, electrolysis, and biomass gasification, each with varying environmental impacts.
Hydrogen’s role as a nonmetal element extends far beyond its simplicity, driving innovation in energy, industry, and sustainability. By understanding its properties and applications, we can harness its potential to build a greener future. Whether for informational curiosity or commercial ventures, hydrogen remains a topic of immense importance. (hydrogen innovation, sustainability, commercial ventures)



