Unlocking Ionization Energies: A Periodic Table Guide

Understanding ionization energies is crucial for anyone delving into the world of chemistry, physics, or materials science. The periodic table serves as a powerful tool to predict and comprehend these energies, which are essential for applications ranging from energy production to chemical synthesis. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or industry professional, this guide will help you unlock the secrets of ionization energies, making complex concepts accessible and actionable.
What is Ionization Energy?

Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in its gaseous state. It’s a key indicator of an element’s reactivity and stability. Elements with low ionization energies tend to lose electrons easily, while those with high ionization energies hold onto them tightly.
💡 Note: Ionization energy increases across a period and decreases down a group in the periodic table.
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy
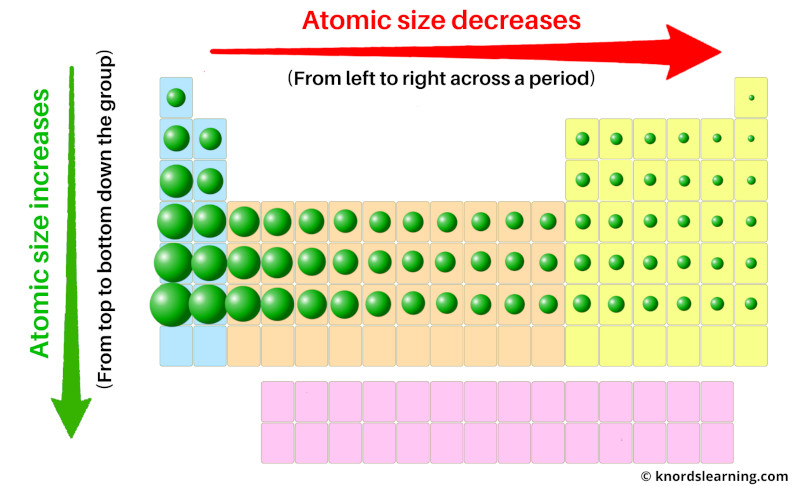
The periodic table is organized in a way that reveals trends in ionization energy. Here’s how to navigate these trends:
Across a Period
As you move from left to right across a period, ionization energy generally increases. This is because the nuclear charge increases, pulling electrons closer to the nucleus.
Down a Group
Moving down a group, ionization energy decreases. This is due to the addition of electron shells, which increase the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
| Trend | Direction | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Across a Period | Increases | Higher Nuclear Charge |
| Down a Group | Decreases | Increased Electron Shells |

Practical Applications of Ionization Energy
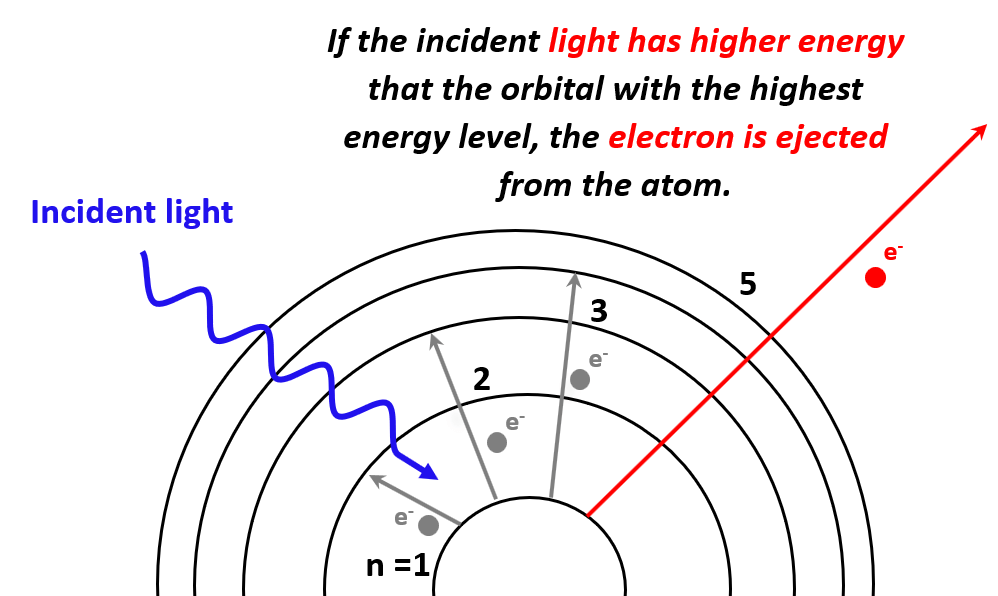
Understanding ionization energies has real-world implications. Here are some key applications:
- Energy Production: Elements with low ionization energies are ideal for use in solar cells and batteries.
- Chemical Synthesis: Predicting reactivity helps in designing efficient chemical reactions.
- Material Science: High ionization energy elements are used in durable materials like ceramics and alloys.
How to Use the Periodic Table for Ionization Energy
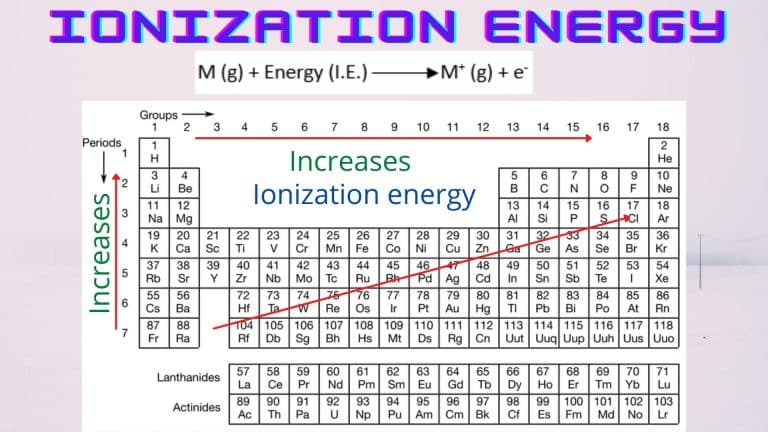
Follow these steps to predict ionization energies using the periodic table:
- Identify the Element’s Position: Locate the element on the periodic table.
- Analyze Trends: Determine if it’s easier to remove an electron based on its position.
- Compare with Neighbors: Compare its ionization energy with adjacent elements.
📌 Note: Exceptions exist, such as the higher ionization energy of boron compared to beryllium due to electron configuration.
Checklist for Mastering Ionization Energies
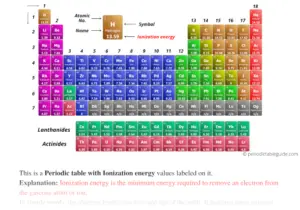
- Learn Periodic Trends: Understand how ionization energy changes across periods and groups.
- Practice Predictions: Use the periodic table to predict ionization energies for various elements.
- Explore Applications: Study how ionization energy impacts real-world technologies.
By mastering these concepts, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the periodic table’s role in chemistry and beyond.
What is the definition of ionization energy?
+Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in its gaseous state.
How does ionization energy change across the periodic table?
+Ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Why is ionization energy important in chemistry?
+It helps predict an element’s reactivity, stability, and suitability for various applications like energy production and material science.
In summary, the periodic table is an invaluable tool for understanding ionization energies. By grasping the trends and exceptions, you can predict elemental behavior and apply this knowledge in diverse fields. Whether for academic study or industrial innovation, mastering ionization energies opens doors to new possibilities. periodic trends,chemical reactivity,energy production,material science,element behavior.



