Kinetic vs Thermodynamic Products: Key Differences Explained
In the world of chemistry, understanding the difference between kinetic vs thermodynamic products is crucial for both students and professionals. These concepts play a significant role in chemical reactions, influencing the outcome and efficiency of processes. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast or a researcher, grasping these principles can enhance your understanding of reaction mechanisms and product formation. Let’s dive into the key differences and why they matter.
What Are Kinetic Products?
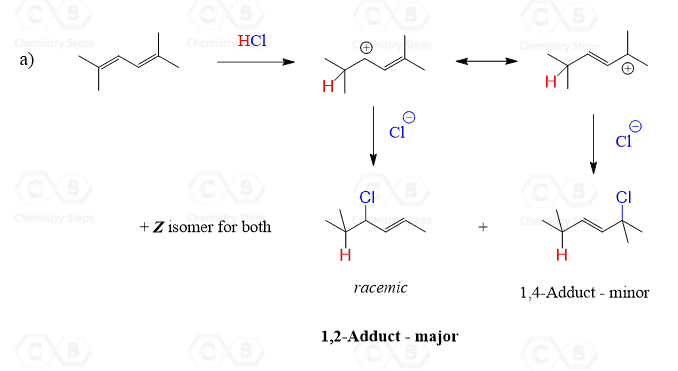
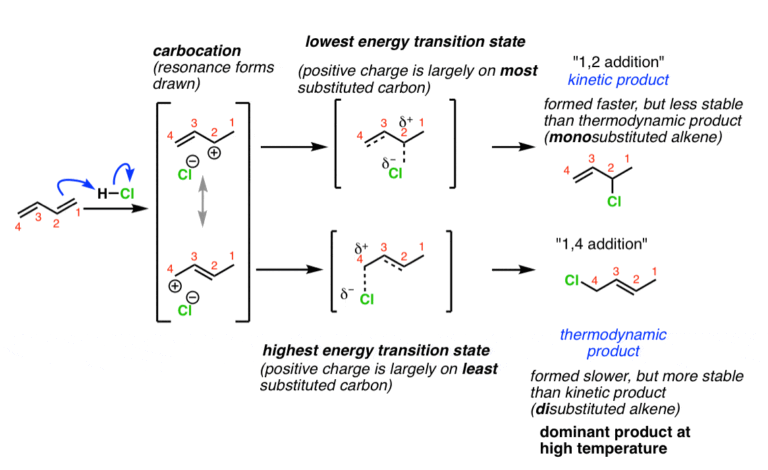
Kinetic products are formed during a chemical reaction based on the fastest reaction pathway, regardless of stability. These products are often the result of reactions that occur quickly under specific conditions. The key factor here is reaction rate, not the overall energy stability of the product.
- Formation: Determined by the lowest energy barrier (activation energy).
- Stability: Not necessarily the most stable product.
- Example: In certain organic reactions, kinetic products form rapidly due to favorable intermediates.
💡 Note: Kinetic products are favored in low-temperature conditions where reactions are less likely to overcome higher energy barriers.
What Are Thermodynamic Products?

Thermodynamic products, on the other hand, are the most stable products formed in a reaction, regardless of how long it takes. These products are determined by the overall energy of the system, favoring the lowest-energy state.
- Formation: Based on the most energetically favorable outcome.
- Stability: Always the most stable product.
- Example: In many reactions, thermodynamic products dominate at higher temperatures or over longer reaction times.
⚛️ Note: Thermodynamic products are often the desired outcome in industrial processes due to their stability.
Key Differences Between Kinetic and Thermodynamic Products
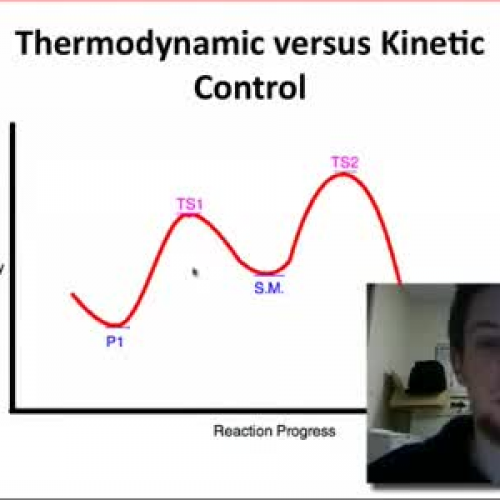
To better understand the contrast, let’s compare the two in a table:
| Aspect | Kinetic Products | Thermodynamic Products |
|---|---|---|
| Formation Basis | Reaction rate (speed) | Overall energy stability |
| Stability | Less stable | Most stable |
| Reaction Conditions | Low temperature, short time | High temperature, long time |

When to Choose Kinetic vs Thermodynamic Products

The choice between kinetic and thermodynamic products depends on the desired outcome and reaction conditions.
- Choose Kinetic Products: When speed is critical, or when specific intermediates are needed for further reactions.
- Choose Thermodynamic Products: When long-term stability and energy efficiency are the primary goals.
🛠️ Note: In some cases, chemists manipulate conditions to favor one product over the other, depending on the application.
Practical Applications

Understanding these concepts is essential in various fields:
- Pharmaceuticals: Controlling product formation ensures the synthesis of the desired drug compound.
- Materials Science: Thermodynamic products are often preferred for durable materials.
- Catalysis: Catalysts can influence whether kinetic or thermodynamic products form.
Checklist for Identifying Kinetic vs Thermodynamic Products
Use this checklist to determine which product is forming in your reaction:
- Reaction Time: Short time? Likely kinetic. Long time? Likely thermodynamic.
- Temperature: Low temperature favors kinetic products; high temperature favors thermodynamic products.
- Stability: Check if the product is the most stable form. If not, it’s likely kinetic.
To summarize, kinetic vs thermodynamic products differ primarily in their formation basis, stability, and reaction conditions. Kinetic products form quickly due to low activation energy, while thermodynamic products are the most stable and form under conditions favoring energy minimization. By understanding these differences, chemists can better control reaction outcomes for various applications.
What determines whether a kinetic or thermodynamic product forms?
+The reaction conditions, such as temperature and time, determine whether a kinetic or thermodynamic product forms. Kinetic products favor speed, while thermodynamic products favor stability.
Can a reaction produce both kinetic and thermodynamic products?
+Yes, depending on the conditions, a reaction can initially produce kinetic products, which may later convert to thermodynamic products over time or under different conditions.
Why are thermodynamic products more stable?
+Thermodynamic products are more stable because they represent the lowest energy state of the system, making them energetically favorable in the long term.
chemical reactions,product formation,reaction mechanisms,reaction rate,energy stability,chemical processes,organic chemistry,industrial chemistry,catalysis,pharmaceutical chemistry,material science,reaction conditions,activation energy,intermediates,energy minimization.


