Left vs Right Tailed Test: Understanding the Difference

When conducting hypothesis testing in statistics, understanding the difference between a left-tailed test and a right-tailed test is crucial. These tests determine the direction of the alternative hypothesis and influence how you interpret results. Whether you're a student, researcher, or data analyst, grasping this concept is essential for accurate statistical analysis. Let’s dive into the details to clarify these terms and their applications, ensuring you can confidently choose the right test for your data.
What is a Left-Tailed Test?
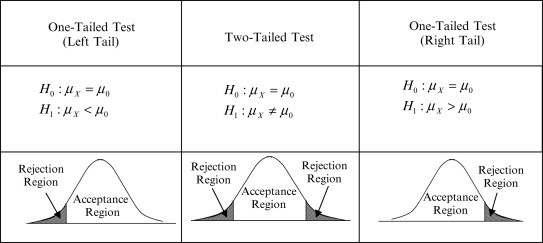
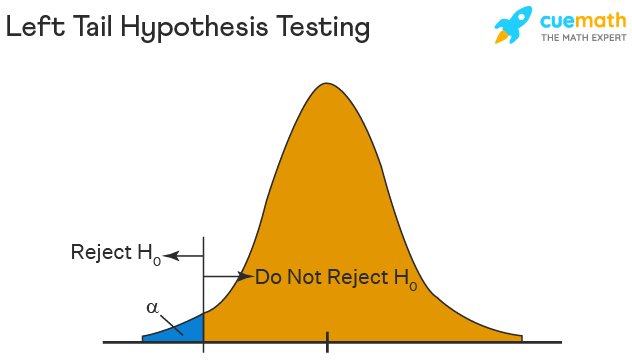
A left-tailed test, also known as a lower-tailed test, is used when the alternative hypothesis suggests that the population parameter is less than a specified value. In this test, the rejection region is on the left side of the distribution curve. For example, if you’re testing whether the average weight of a product is less than 10 kg, you’d use a left-tailed test.
📊 Note: Always ensure your alternative hypothesis aligns with the direction of the tail you’re testing.
What is a Right-Tailed Test?

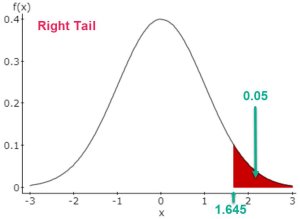
A right-tailed test, or upper-tailed test, is applied when the alternative hypothesis indicates that the population parameter is greater than a specified value. Here, the rejection region is on the right side of the distribution curve. For instance, if you’re testing whether the average lifespan of a battery exceeds 100 hours, a right-tailed test is appropriate.
Key Differences Between Left and Right-Tailed Tests
| Aspect | Left-Tailed Test | Right-Tailed Test |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative Hypothesis | Parameter < specified value | Parameter > specified value |
| Rejection Region | Left side of the distribution | Right side of the distribution |
| Example | Testing if a mean is less than 50 | Testing if a mean is greater than 50 |
When to Use Each Test
- Left-Tailed Test: Use when you want to determine if a parameter is significantly lower than a hypothesized value.
- Right-Tailed Test: Use when you want to determine if a parameter is significantly higher than a hypothesized value.
💡 Note: Always clearly define your hypothesis before choosing the test direction.
Checklist for Choosing the Right Test
- Identify the alternative hypothesis.
- Determine if the parameter is less than or greater than the specified value.
- Select the corresponding tail (left or right) based on the hypothesis.
- Verify the rejection region aligns with the chosen tail.
In summary, left-tailed tests and right-tailed tests are fundamental concepts in hypothesis testing, each serving a specific purpose based on the direction of the alternative hypothesis. By understanding these differences, you can ensure accurate statistical analysis and reliable results. Remember to always align your hypothesis with the appropriate tail direction for precise testing.
What is the main difference between a left-tailed and right-tailed test?
+The main difference lies in the direction of the alternative hypothesis. A left-tailed test checks if a parameter is less than a value, while a right-tailed test checks if it’s greater.
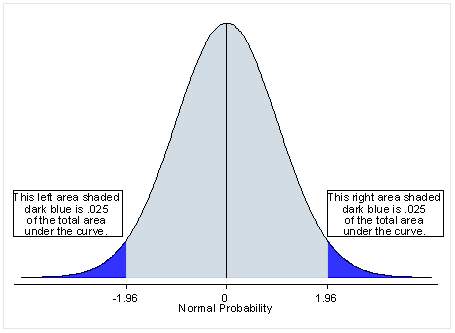
Can I use a two-tailed test instead of a left or right-tailed test?
+Yes, a two-tailed test is used when the alternative hypothesis does not specify a direction, testing for both greater and lesser values.
How do I determine which tailed test to use?
+Determine the direction of your alternative hypothesis. If it suggests "less than," use a left-tailed test; if "greater than," use a right-tailed test.
hypothesis testing, statistical analysis, rejection region, alternative hypothesis, distribution curve, two-tailed test, statistical significance, data analysis,left-tailed test vs right-tailed test,statistical hypothesis testing