Uncover the Secrets of Lone Electron Pairs Lone Electron Pairs: What You Need to Know Mastering Lone Electron Pairs in Chemistry Lone Electron Pairs Explained Simply The Role of Lone Electron Pairs in Molecules
Lone electron pairs, often referred to as non-bonding electron pairs, play a crucial role in chemistry, influencing molecular geometry, reactivity, and properties. Understanding these elusive pairs is essential for students, researchers, and professionals alike. Whether you're studying Lone Electron Pairs in Chemistry or exploring their applications in Molecular Structure, this guide will help you master the concept. Let’s dive into the world of lone electron pairs and uncover their secrets, from their definition to their impact on chemical behavior.
What Are Lone Electron Pairs?

Lone electron pairs are pairs of valence electrons that are not involved in bonding but remain associated with an atom. They are typically found in the outermost shell of an atom and are crucial in determining a molecule’s shape and reactivity. For instance, in Ammonia (NH₃), the nitrogen atom has one lone pair, which affects its geometry and chemical properties.
📌 Note: Lone pairs are often represented in Lewis structures as two dots adjacent to an atom.
The Role of Lone Electron Pairs in Molecules

Molecular Geometry
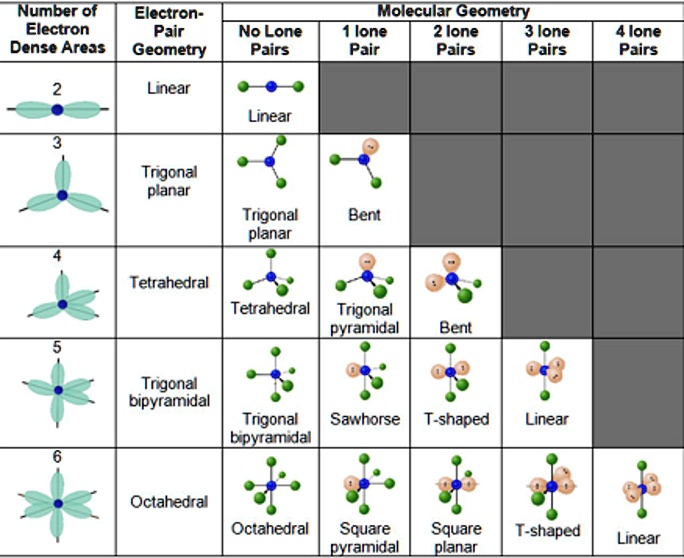
Lone pairs repel bonded pairs, altering the shape of molecules. This phenomenon is explained by the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory. For example, water (H₂O) has two lone pairs on the oxygen atom, resulting in a bent shape.
Chemical Reactivity
Lone pairs can participate in chemical reactions, acting as nucleophiles. They are involved in processes like Nucleophilic Substitution and Base Catalysis. Understanding their role is key to predicting reaction outcomes.
Mastering Lone Electron Pairs in Chemistry

To master lone electron pairs, follow these steps:
- Learn Lewis Structures: Practice drawing Lewis structures to identify lone pairs.
- Apply VSEPR Theory: Use VSEPR to predict molecular geometry based on lone pairs.
- Study Examples: Analyze molecules like ammonia, water, and chlorine trifluoride (ClF₃) to understand lone pair effects.
Lone Electron Pairs Explained Simply

Think of lone electron pairs as “solo dancers” on an atom. While other electrons are busy bonding, these pairs stay unpaired, influencing the molecule’s behavior. Their presence can make a molecule more reactive or change its shape entirely.
Checklist: Key Takeaways
- Lone pairs are non-bonding valence electrons.
- They affect molecular geometry via VSEPR theory.
- Lone pairs play a role in chemical reactivity.
- Mastering Lewis structures is essential for understanding lone pairs.
In summary, lone electron pairs are fundamental to chemistry, shaping molecular structures and driving reactions. By understanding their role and behavior, you can predict chemical outcomes and excel in your studies or research. Whether you're a student or a professional, mastering lone pairs is a valuable skill in the world of chemistry.
What is the difference between lone pairs and bonding pairs?
+Lone pairs are non-bonding electrons associated with an atom, while bonding pairs are electrons shared between atoms to form chemical bonds.
How do lone pairs affect molecular geometry?
+Lone pairs repel bonding pairs, causing molecules to adopt specific shapes as predicted by the VSEPR theory.
Can lone pairs participate in chemical reactions?
+Yes, lone pairs can act as nucleophiles and participate in reactions like nucleophilic substitution and base catalysis.
Lone Electron Pairs in Chemistry, Molecular Structure, VSEPR Theory, Nucleophilic Substitution, Chemical Reactivity, Lewis Structures, Ammonia, Water Molecule, Chemical Bonding, Valence Electrons.