Lysosome Function in Plant Cells: Unlocking Cellular Secrets
Plant cells are marvels of nature, housing intricate structures that work in harmony to sustain life. Among these, the lysosome plays a pivotal role in cellular function, often referred to as the cell's recycling center. Understanding lysosome function in plant cells not only unlocks cellular secrets but also sheds light on plant health, growth, and responses to stress. Whether you're a botanist, a student, or simply curious about plant biology, this guide dives deep into the world of lysosomes, their importance, and how they contribute to plant vitality.
What is a Lysosome and Its Role in Plant Cells?

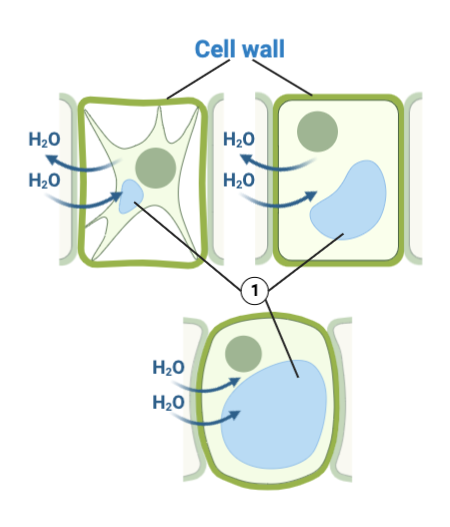
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in both animal and plant cells. In plants, they are often referred to as vacuoles, which perform similar functions. These organelles are responsible for cellular waste management, breaking down damaged or worn-out cellular components, and recycling their contents. This process, known as autophagy, is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring plant health.
Key Functions of Lysosomes in Plant Cells
- Waste Degradation: Lysosomes break down proteins, lipids, and other macromolecules into reusable components.
- Stress Response: They help plants cope with environmental stressors like drought, salinity, and pathogens.
- Nutrient Recycling: By recycling cellular materials, lysosomes ensure plants have the nutrients needed for growth.
Understanding these functions is essential for anyone studying plant cell biology or exploring ways to enhance crop resilience. By focusing on lysosomes, researchers can develop strategies to improve plant health and productivity, especially in challenging environments.
How Lysosomes Contribute to Plant Health and Growth

Lysosomes are not just waste processors; they are vital for plant development and survival. Their ability to recycle nutrients and respond to stress makes them indispensable in plant growth mechanisms. For instance, during seed germination, lysosomes break down stored proteins and lipids to provide energy for the growing seedling.
Lysosomes and Plant Stress Tolerance
In adverse conditions, lysosomes activate autophagy pathways to protect plants. This process helps cells remove damaged organelles and proteins, preventing cellular damage. For farmers and agronomists, understanding this mechanism can lead to the development of stress-tolerant crops, ensuring better yields in challenging climates.
| Function | Benefit to Plant |
|---|---|
| Waste Degradation | Maintains cellular cleanliness |
| Stress Response | Enhances resilience to environmental stressors |
| Nutrient Recycling | Supports growth and development |

📌 Note: Lysosomes in plant cells are often larger and more complex than their animal counterparts, reflecting their diverse roles in plant physiology.
In summary, lysosomes are essential organelles that drive cellular recycling, stress tolerance, and nutrient management in plant cells. By studying their functions, we can unlock new ways to improve plant health and productivity. Whether you're researching plant biology or looking for solutions to agricultural challenges, understanding lysosomes is a step toward harnessing the full potential of plant cells.
What is the main function of lysosomes in plant cells?
+Lysosomes in plant cells primarily function as recycling centers, breaking down waste materials and recycling nutrients to support cellular processes.
How do lysosomes help plants during stress?
+Lysosomes activate autophagy pathways during stress, removing damaged cellular components and protecting the plant from further harm.
Are lysosomes the same in plants and animals?
+While lysosomes perform similar functions in both, plant lysosomes (often called vacuoles) are larger and more complex, reflecting their additional roles in plant physiology.
plant cell biology, autophagy in plants, cellular recycling, plant stress tolerance, lysosome function, plant growth mechanisms,keyword/title,keyword/title,etc.