Medullary Cavity Explained: Bone Structure Simplified

The medullary cavity is a vital component of bone anatomy, often overlooked but crucial for bone health and function. Located in the center of long bones, it houses essential tissues and plays a key role in nutrient supply and waste removal. Understanding its structure and function can provide valuable insights into bone biology, bone structure, and related conditions. Whether you're a student, healthcare professional, or simply curious about human anatomy, this guide simplifies the medullary cavity's role in maintaining skeletal integrity.
What is the Medullary Cavity? (Bone Marrow, Skeletal System)

The medullary cavity is the hollow region within the diaphysis (shaft) of long bones, such as the femur or humerus. It is primarily filled with bone marrow, a soft, spongy tissue responsible for producing blood cells. This cavity is surrounded by dense cortical bone, which provides structural support and protection.
Key Functions of the Medullary Cavity (Blood Cell Production, Nutrient Supply)

- Blood Cell Production: The medullary cavity contains red bone marrow, which produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Nutrient Supply: It facilitates the transport of nutrients and oxygen to bone tissues via blood vessels.
- Waste Removal: It aids in removing metabolic waste products from bone cells.
Types of Bone Marrow in the Medullary Cavity (Red Bone Marrow, Yellow Bone Marrow)

| Type | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Red Bone Marrow | Found in flat bones and ends of long bones | Active in blood cell production |
| Yellow Bone Marrow | Primarily in the medullary cavity of long bones | Stores fat and provides energy reserves |
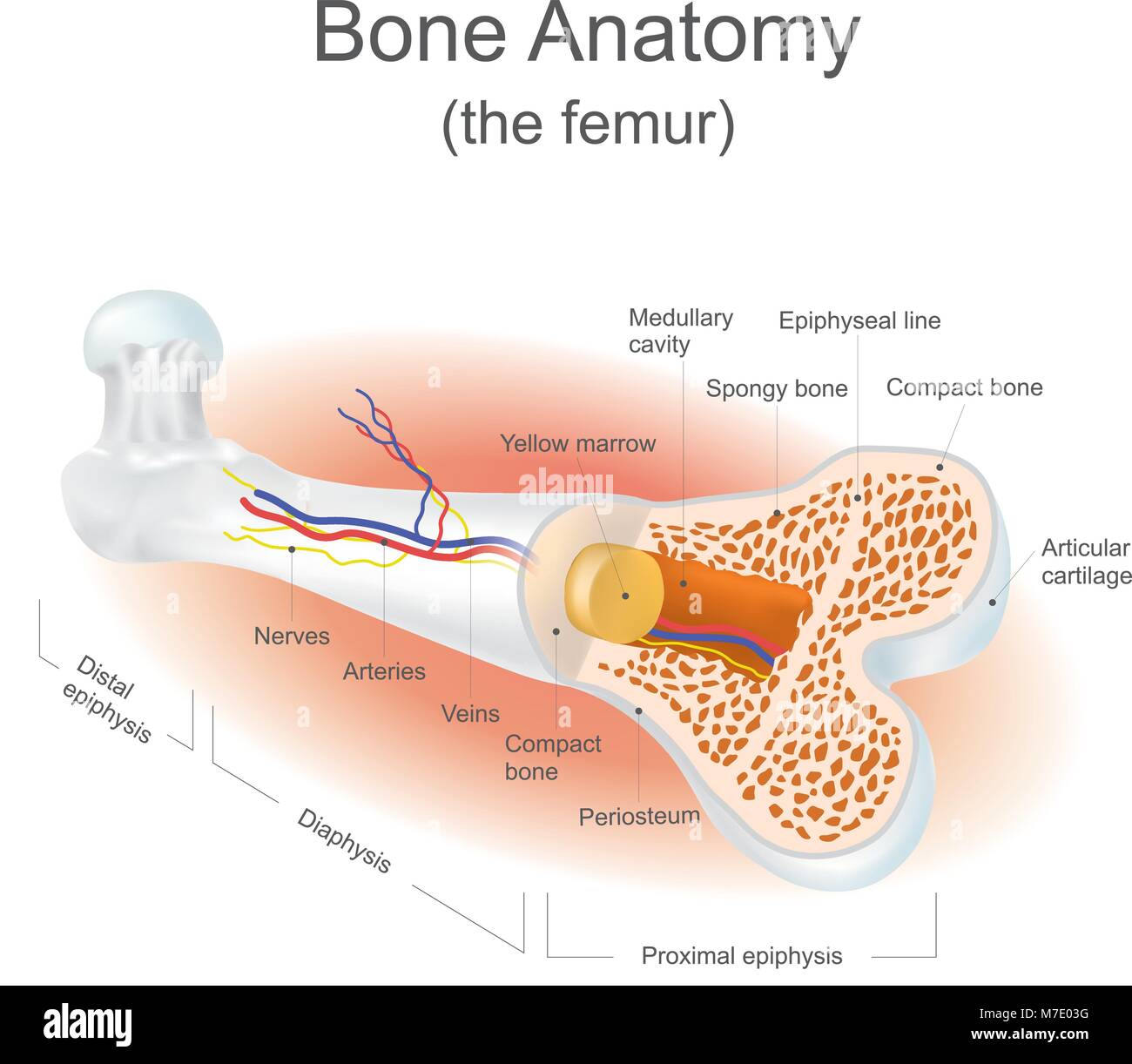
💡 Note: Yellow bone marrow can convert back to red bone marrow under certain conditions, such as severe blood loss.
Clinical Significance of the Medullary Cavity (Bone Marrow Transplant, Osteoporosis)

The medullary cavity is often involved in medical procedures like bone marrow transplants, where healthy marrow is introduced to treat conditions such as leukemia. Additionally, diseases like osteoporosis can affect bone density, impacting the cavity’s structure and function.
Tips for Maintaining Medullary Cavity Health (Calcium, Vitamin D, Exercise)

- Nutrition: Consume adequate calcium and vitamin D to support bone marrow function.
- Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises promote bone density and overall skeletal health.
- Regular Checkups: Monitor bone health through routine medical exams.
Medullary Cavity Health Checklist (Bone Health, Marrow Function)
- Ensure a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D.
- Incorporate weight-bearing exercises into your routine.
- Stay informed about bone health and related conditions.
The medullary cavity is a fascinating yet essential part of our skeletal system, playing a pivotal role in blood cell production and bone health. By understanding its structure and function, we can better appreciate the importance of maintaining strong, healthy bones. Incorporate the tips provided to support your bone health and overall well-being.
What is the primary function of the medullary cavity?
+
The medullary cavity primarily houses bone marrow, which is responsible for producing blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
How does the medullary cavity relate to osteoporosis?
+
Osteoporosis reduces bone density, which can weaken the cortical bone surrounding the medullary cavity, potentially impacting its function and stability.
Can yellow bone marrow convert to red bone marrow?
+
Yes, under certain conditions like severe blood loss, yellow bone marrow can convert back to red bone marrow to increase blood cell production.



