Morula vs Blastocyst: Key Differences Explained

Understanding the early stages of embryonic development is crucial for anyone exploring fertility treatments or interested in reproductive biology. Two key terms often mentioned in this context are morula and blastocyst. While both are early forms of an embryo, they differ significantly in structure, development stage, and potential for implantation. This post will delve into the key differences between morula and blastocyst, providing a clear and informative guide for both informational and commercial-intent audiences.
What is a Morula?
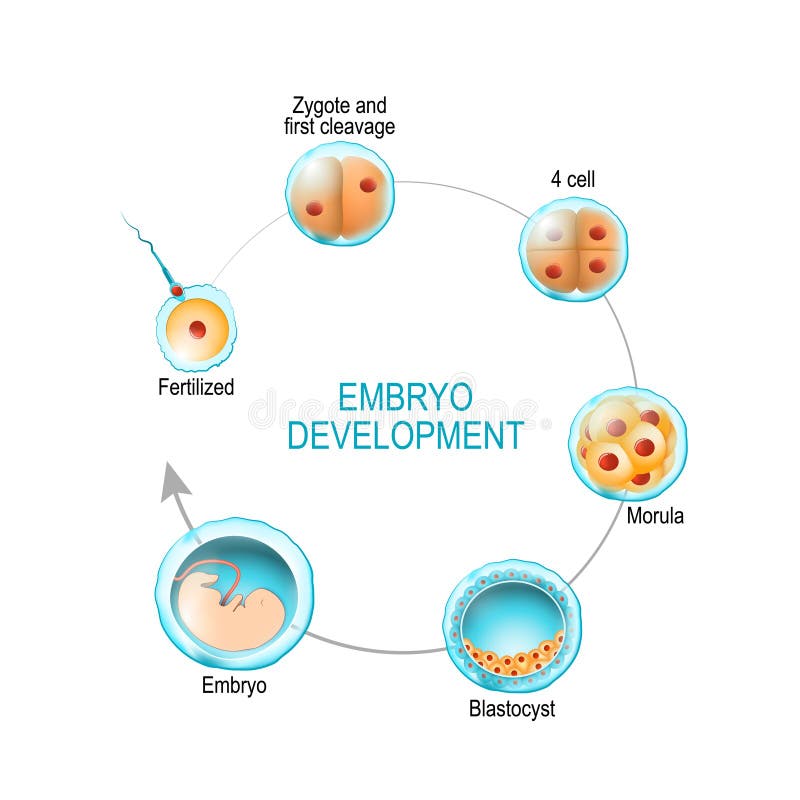
A morula is one of the earliest stages of embryonic development, typically occurring 3–4 days after fertilization. It is a solid mass of cells, resembling a mulberry (hence the name “morula,” derived from the Latin word for mulberry). At this stage, the embryo consists of 16–32 cells and has not yet developed distinct layers or structures.
💡 Note: The morula stage is crucial as it marks the beginning of cell differentiation, preparing the embryo for further growth.
What is a Blastocyst?
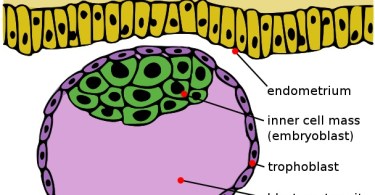
A blastocyst is the next developmental stage after the morula, typically reached 5–6 days after fertilization. It is a more advanced structure, characterized by a fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel and the differentiation of cells into two distinct layers: the trophoblast (outer layer) and the inner cell mass. The trophoblast will eventually form the placenta, while the inner cell mass develops into the fetus.
💡 Note: The blastocyst stage is critical for successful implantation into the uterine lining during pregnancy.
Key Differences Between Morula and Blastocyst

To better understand the distinctions, let’s compare the two stages in a table:
| Feature | Morula | Blastocyst |
|---|---|---|
| Developmental Stage | 3–4 days post-fertilization | 5–6 days post-fertilization |
| Structure | Solid mass of cells | Fluid-filled cavity (blastocoel) with distinct layers |
| Cell Count | 16–32 cells | ~100 cells |
| Implantation Readiness | Not ready for implantation | Ready for implantation into the uterus |
Why These Differences Matter in Fertility Treatments

For those undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF), understanding the difference between morula and blastocyst is essential. Embryos are often cultured to the blastocyst stage before transfer, as this increases the chances of successful implantation. However, in some cases, morula-stage embryos may be transferred, depending on individual circumstances.
💡 Note: Blastocyst transfers are generally preferred due to higher implantation rates, but the decision depends on the embryo’s quality and the patient’s health.
Checklist for Embryo Development Stages
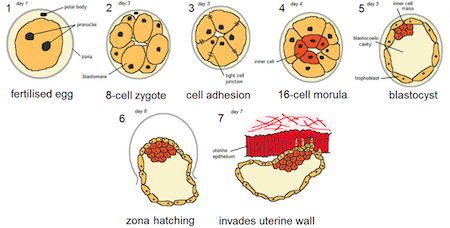
- Morula Stage: Solid mass of 16–32 cells, 3–4 days post-fertilization.
- Blastocyst Stage: Fluid-filled cavity, distinct cell layers, 5–6 days post-fertilization.
- Implantation Readiness: Blastocysts are ready for uterine implantation; morulas are not.
In summary, while both the morula and blastocyst are early embryonic stages, their differences in structure, cell count, and implantation potential are significant. For individuals exploring fertility treatments, understanding these distinctions can provide valuable insights into the IVF process. Whether you’re researching for informational purposes or considering commercial fertility options, knowing the morula vs blastocyst differences is a crucial step in your journey.
What comes first: morula or blastocyst?
+The morula stage comes first, typically 3–4 days after fertilization, followed by the blastocyst stage at 5–6 days.
Can a morula implant in the uterus?
+No, a morula is not ready for implantation. Only a blastocyst, with its distinct layers and fluid-filled cavity, can implant into the uterine lining.
Why are blastocyst transfers preferred in IVF?
+Blastocyst transfers have higher implantation rates because the embryo is more developed and better suited for attachment to the uterus.
(embryonic development, IVF process, fertility treatments, implantation stages)



