PKA for Formic Acid: Key Insights & Applications

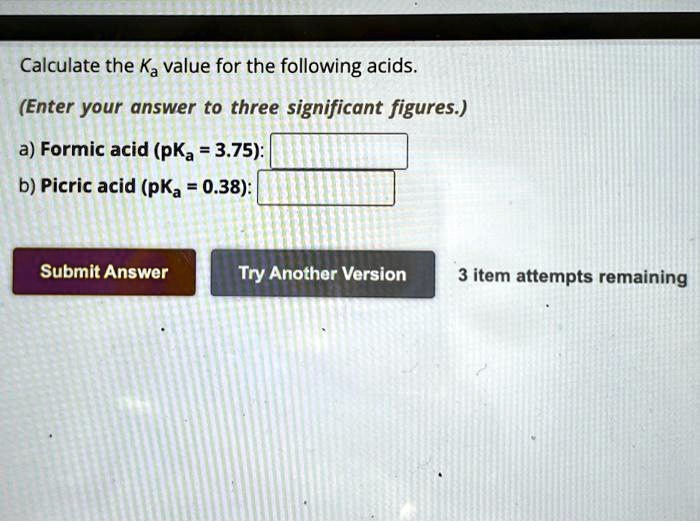
Formic acid, a versatile organic compound, plays a crucial role in various industries, from chemical manufacturing to agriculture. Understanding its PKA (pKa value) is essential for optimizing its applications. The pKa of formic acid, approximately 3.75, defines its acidity and behavior in different solutions. This blog explores PKA for formic acid, its significance, and practical applications, ensuring both informational and commercial audiences gain valuable insights.
What is PKA and Why is it Important for Formic Acid?
PKA, or acid dissociation constant (pKa), measures the strength of an acid in a solution. For formic acid, its pKa value indicates how readily it donates protons (H⁺ ions). This property is vital for understanding its reactivity, solubility, and effectiveness in applications like formic acid preservation, formic acid in cleaning agents, and formic acid in chemical synthesis.
Key Insights into Formic Acid’s PKA
- Acidity Level: With a pKa of 3.75, formic acid is a weak acid, making it safer and more versatile than strong acids.
- pH Influence: Its acidity varies with pH, affecting its use in pH-sensitive processes like food preservation and leather tanning.
- Buffering Capacity: Formic acid’s pKa allows it to act as a buffer in solutions, maintaining stable pH levels in industrial processes.
Practical Applications of Formic Acid Based on Its PKA

The pKa of formic acid makes it an ideal candidate for numerous applications across industries. Here’s how its acidity is leveraged:
Industrial Uses of Formic Acid
| Application | Relevance of PKA |
|---|---|
| Chemical Synthesis | Facilitates reactions by controlling pH and proton availability. |
| Agriculture | Acts as a preservative and pesticide due to its mild acidity. |
| Cleaning Agents | Effectively removes mineral deposits without causing corrosion. |

Formic Acid in Everyday Products
From formic acid in household cleaners to its role in food additives, its pKa ensures safety and efficacy. For instance, it’s used in:
- Descaling coffee machines.
- Preserving silage in agriculture.
- Acting as an antibacterial agent in food processing.
📌 Note: Always handle formic acid with care, as its acidity can cause skin and eye irritation.
Summary: Key Takeaways on Formic Acid’s PKA
Formic acid’s pKa of 3.75 is central to its applications in industrial processes, agriculture, and household products. Its weak acidity makes it a safer alternative for various uses. Below is a checklist to maximize its benefits:
- Verify pH requirements for your application.
- Use formic acid in controlled quantities to avoid overexposure.
- Leverage its buffering capacity for pH-sensitive processes.
In summary, understanding the PKA for formic acid unlocks its potential across industries. Whether for chemical synthesis, agriculture, or cleaning, its acidity ensures efficiency and safety. By leveraging this knowledge, businesses and individuals can optimize formic acid’s use in their processes, formic acid preservation, formic acid in cleaning agents, formic acid in chemical synthesis.
What is the pKa of formic acid?
+
The pKa of formic acid is approximately 3.75, classifying it as a weak acid.
How does formic acid’s pKa affect its applications?
+
Its pKa determines its acidity, making it suitable for pH-sensitive processes like preservation and cleaning.
Is formic acid safe for household use?
+
Yes, when used in controlled quantities, formic acid is safe for household applications like cleaning.


