Positive vs Negative Control: Understanding the Key Differences

In the world of experiments and research, controls play a crucial role in ensuring the validity and reliability of results. Two key types of controls, positive control and negative control, are often used to verify that an experiment is functioning correctly. Understanding the differences between these controls is essential for anyone involved in scientific research, quality control, or even everyday problem-solving. This post will delve into the key distinctions between positive and negative controls, their applications, and why they matter. (Positive vs Negative Control, Experimental Design, Scientific Research)
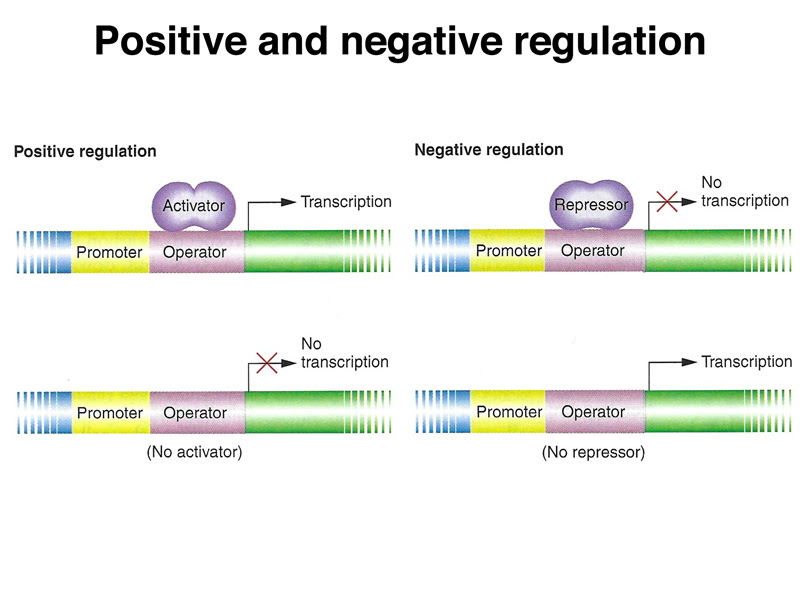
What is a Positive Control?

A positive control is a sample or condition in an experiment that is known to produce a positive result. It serves as a benchmark to confirm that the experimental setup is working as expected. For instance, in a drug efficacy test, a positive control would be a substance known to effectively treat the condition being studied. If the positive control fails to show the expected outcome, it indicates a problem with the experimental design or execution.
Key Characteristics of Positive Control
- Expected Outcome: Always produces a known, positive result.
- Purpose: Validates the experimental procedure.
- Example: Using penicillin as a positive control in an antibiotic sensitivity test.
What is a Negative Control?

In contrast, a negative control is a sample or condition that is expected to produce no effect or a negative result. It helps ensure that any observed effects in the experimental group are due to the variable being tested and not external factors. For example, in a chemical reaction experiment, a negative control might involve using distilled water instead of the reactive substance.
Key Characteristics of Negative Control
- Expected Outcome: Produces no effect or a negative result.
- Purpose: Rules out false positives and confirms the specificity of the experiment.
- Example: Using a placebo in a clinical trial to compare against the actual treatment.
Comparing Positive and Negative Controls

To better understand the differences, let’s compare the two in a table:
| Aspect | Positive Control | Negative Control |
|---|---|---|
| Expected Result | Positive | Negative |
| Purpose | Validates experimental setup | Ensures specificity and rules out false positives |
| Example | Penicillin in antibiotic test | Placebo in clinical trial |
💡 Note: Both controls are essential for robust experimental design, ensuring that results are both reliable and meaningful.
When to Use Positive vs Negative Control

- Use Positive Control When: You need to confirm that your experimental conditions are capable of detecting the expected outcome.
- Use Negative Control When: You want to ensure that any observed effects are not due to contamination, external factors, or experimental error.
Checklist for Implementing Controls
- [ ] Identify the purpose: Determine whether you need to validate the setup (positive control) or rule out false positives (negative control).
- [ ] Select appropriate samples: Choose known positive and negative samples relevant to your experiment.
- [ ] Run controls alongside experiments: Ensure controls are tested under the same conditions as the experimental groups.
- [ ] Analyze results: Compare control outcomes to experimental results to draw accurate conclusions.
Why Controls Matter

Controls are the backbone of scientific research, ensuring that experiments are both accurate and reproducible. Without them, it’s difficult to determine whether the results are due to the variable being tested or other factors. Whether you’re conducting a lab experiment, a clinical trial, or even a marketing campaign, understanding and applying positive and negative controls can significantly enhance the reliability of your findings. (Experimental Validity, Research Methodology, Quality Control)
What is the main purpose of a positive control?
+A positive control is used to validate that the experimental setup is functioning correctly by producing a known, positive result.
Why is a negative control important?
+A negative control ensures that any observed effects in the experimental group are not due to external factors or contamination, ruling out false positives.
Can an experiment have both positive and negative controls?
+Yes, many experiments include both types of controls to ensure comprehensive validation and specificity of results.
In summary, positive controls and negative controls are indispensable tools in experimental design, each serving distinct purposes. By understanding their differences and applications, researchers and professionals can enhance the accuracy and reliability of their work. Whether you’re validating a new drug, testing a chemical reaction, or analyzing data, controls are your allies in achieving robust and trustworthy results. (Scientific Methodology, Control Groups, Research Integrity)


