Weak Base Strong Acid Titration: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the principles of weak base strong acid titration is essential for students, researchers, and professionals in chemistry. This process involves the neutralization of a weak base by a strong acid, leading to a measurable pH change. Whether you're conducting experiments in a lab or preparing for an exam, mastering this technique will enhance your analytical skills. Below, we’ll explore the step-by-step process, key concepts, and practical tips to ensure accurate results. (acid-base titration, chemical analysis, pH measurement)
What is Weak Base Strong Acid Titration?
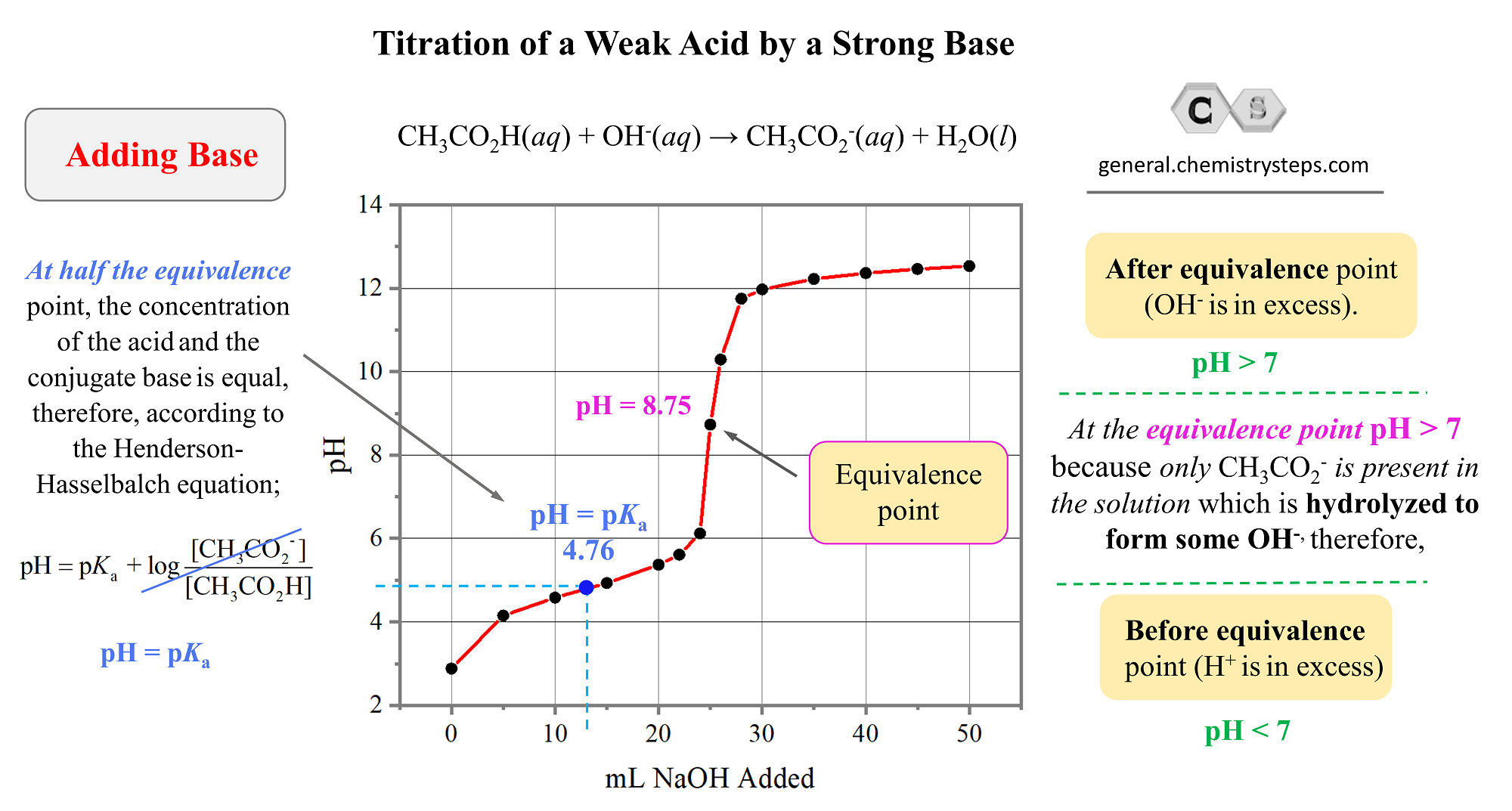
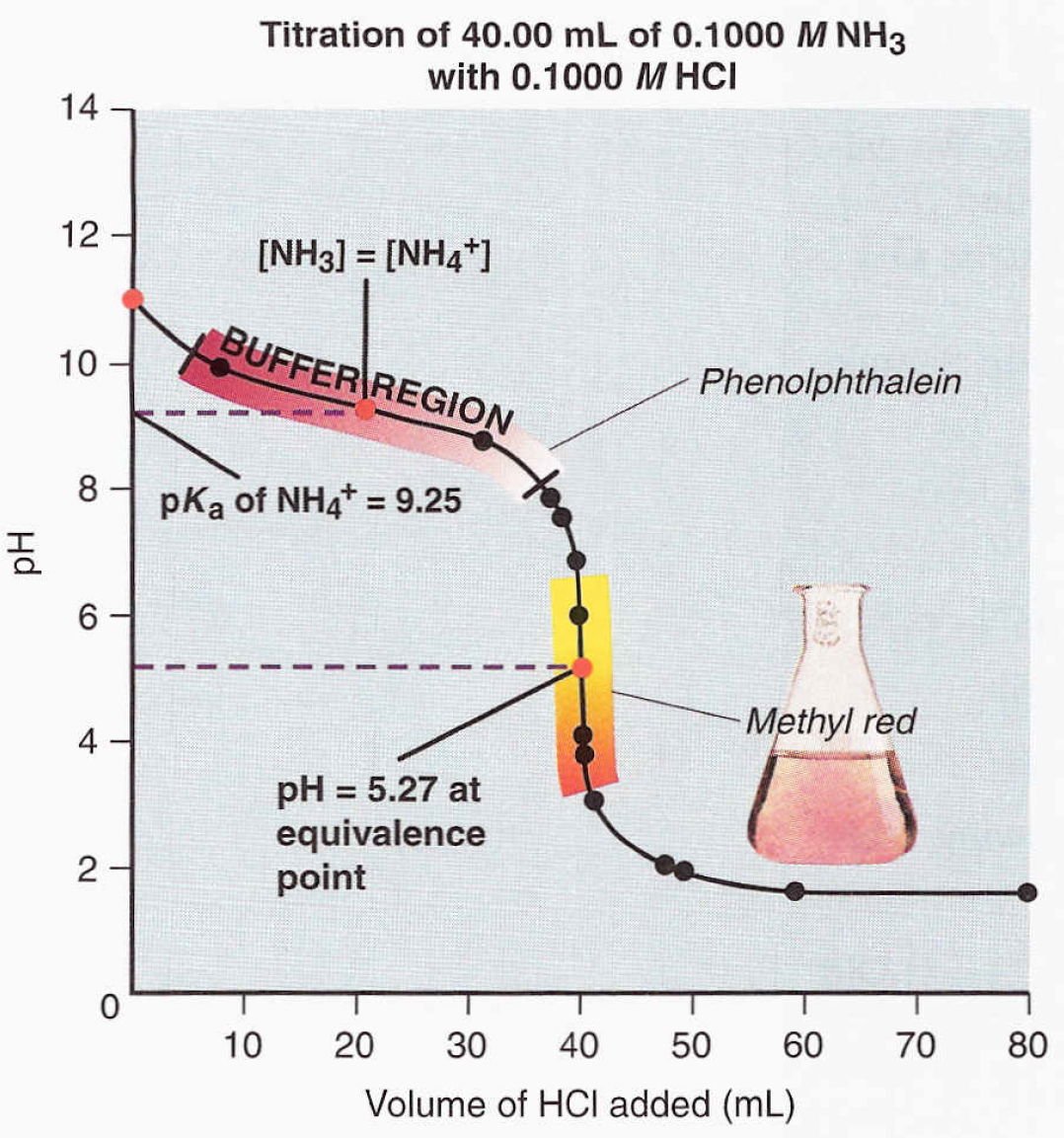
A weak base strong acid titration is a type of acid-base titration where a weak base, such as ammonia (NH₃), is titrated against a strong acid, like hydrochloric acid (HCl). The reaction produces a salt and water, with a noticeable pH shift at the equivalence point. This titration is crucial for determining the concentration of the weak base. (titration process, equivalence point, pH shift)
Key Concepts in Weak Base Strong Acid Titration
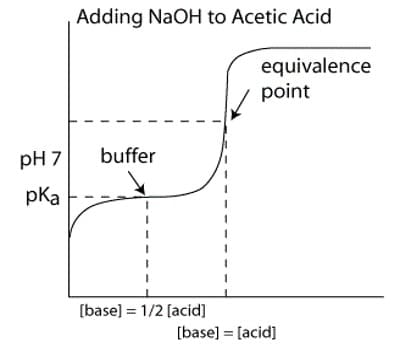
1. Equivalence Point vs. Endpoint
The equivalence point is when the moles of acid equal the moles of base, while the endpoint is the point at which the indicator changes color. Understanding the difference is vital for accurate results. (equivalence point, endpoint, acid-base reaction)
2. pH Changes During Titration
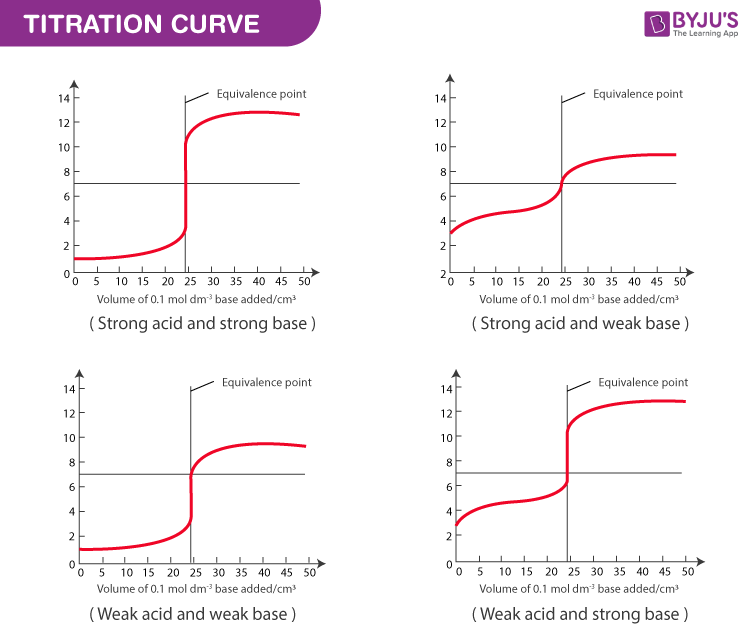
During the titration, the pH starts high due to the weak base and gradually decreases as the strong acid is added. At the equivalence point, the pH depends on the salt formed. For example, NH₄Cl (from NH₃ and HCl) forms an acidic solution. (pH changes, titration curve, acidic solution)
Step-by-Step Procedure for Weak Base Strong Acid Titration

1. Prepare the Solutions
- Measure the volume of the weak base solution.
- Standardize the strong acid solution using a primary standard like sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃).
2. Set Up the Titration
- Place the weak base in a beaker or Erlenmeyer flask.
- Add a few drops of a suitable indicator (e.g., bromothymol blue) or use a pH meter.
3. Perform the Titration
- Slowly add the strong acid from a burette while stirring continuously.
- Record the volume of acid added until the endpoint is reached.
📌 Note: Ensure proper mixing to achieve accurate results.
4. Analyze the Results
Plot a titration curve to visualize pH changes and determine the equivalence point. Calculate the concentration of the weak base using the formula:
M₁V₁ = M₂V₂, where M₁ and V₁ are the molarity and volume of the acid, and M₂ and V₂ are the molarity and volume of the base. (titration curve, concentration calculation, molarity)
| Weak Base | Strong Acid |
|---|---|
| Ammonia (NH₃) | Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) |
| Methylamine (CH₃NH₂) | Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) |
Checklist for Successful Titration
- Standardize the strong acid solution.
- Use a suitable indicator or pH meter.
- Stir continuously during titration.
- Record precise volumes and pH readings.
- Plot and analyze the titration curve.
Mastering weak base strong acid titration is a valuable skill in chemistry. By understanding the principles, following the correct procedure, and analyzing results accurately, you can achieve precise measurements. Whether for academic or professional purposes, this guide ensures you’re well-equipped to handle titration experiments effectively. (acid-base reactions, titration techniques, chemical analysis)
What is the difference between a weak base and a strong base in titration?
+
A weak base only partially dissociates in water, while a strong base fully dissociates. This affects the pH changes and titration curve during the experiment. (weak base, strong base, pH changes)
Why is a strong acid used in weak base titration?
+
A strong acid ensures complete neutralization of the weak base, making it easier to determine the equivalence point and calculate the base’s concentration. (strong acid, neutralization, equivalence point)
How do I choose the right indicator for this titration?
+
Select an indicator with a pH range that includes the equivalence point. For weak base strong acid titration, bromothymol blue or phenolphthalein are commonly used. (indicator selection, pH range, equivalence point)