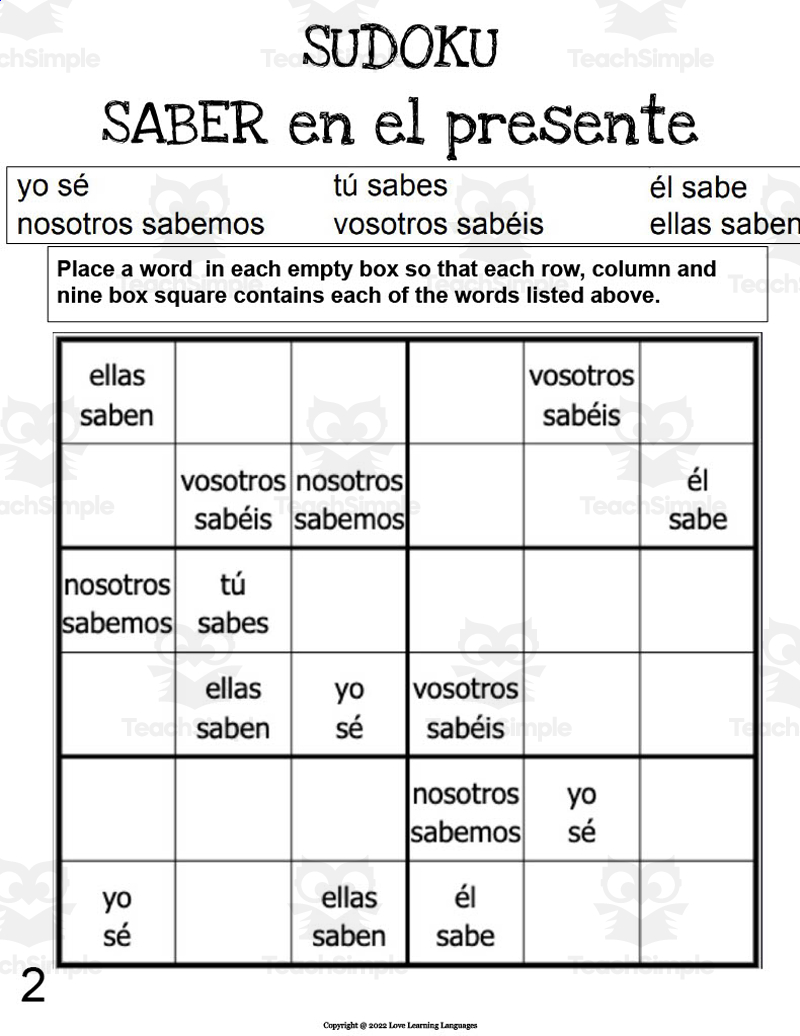
What Charge Does DNA Carry?

DNA, the blueprint of life, is a complex molecule that carries genetic information. But have you ever wondered, "What charge does DNA carry?" This question is crucial for understanding DNA's structure, function, and interactions within the cell. In this post, we'll explore the electrical properties of DNA, its charge characteristics, and why it matters in biology and biotechnology. (DNA charge, DNA structure, molecular biology)
Understanding DNA’s Charge: A Fundamental Concept

DNA is a negatively charged molecule due to the presence of phosphate groups in its backbone. These phosphate groups give DNA its overall negative charge, which plays a vital role in its interactions with other molecules. (DNA charge, phosphate groups, molecular interactions)
The Role of Phosphate Groups in DNA Charge
Each phosphate group in the DNA backbone carries a negative charge at physiological pH. This negative charge is essential for DNA’s stability, replication, and transcription processes. The charge also influences how DNA interacts with proteins and other molecules in the cell. (phosphate groups, DNA stability, protein interactions)
How DNA’s Charge Affects Its Function

The negative charge of DNA has significant implications for its biological functions. Here are some key aspects:
- DNA Packaging: The negative charge helps DNA wrap around histone proteins, facilitating its packaging into chromatin and chromosomes. (DNA packaging, histone proteins, chromatin structure)
- DNA Replication: During replication, the negative charge ensures proper alignment and separation of DNA strands. (DNA replication, strand separation, molecular biology)
- Gene Expression: The charge influences how transcription factors and enzymes bind to DNA, regulating gene expression. (gene expression, transcription factors, enzymatic binding)
DNA Charge in Biotechnology
Understanding DNA’s charge is also crucial in biotechnology applications. For instance, in DNA electrophoresis, the negative charge allows DNA fragments to migrate towards a positive electrode, enabling their separation and analysis. (DNA electrophoresis, fragment separation, biotechnology applications)
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Charge Source | Phosphate groups in DNA backbone |
| Charge at pH 7 | Negative (-) |
| Biological Significance | Stability, replication, transcription, and packaging |

📌 Note: The charge of DNA can be influenced by factors like pH, ionic strength, and the presence of counterions. These factors can affect DNA's behavior in experimental settings and biological processes. (pH effects, ionic strength, counterions)
Key Takeaways: DNA Charge Essentials

To summarize, DNA carries a negative charge due to its phosphate groups, which is fundamental to its structure and function. Here’s a quick checklist of key points:
- DNA is negatively charged due to phosphate groups.
- The charge is crucial for DNA packaging, replication, and gene expression.
- Understanding DNA charge is essential for biotechnology applications like electrophoresis.
Why is DNA negatively charged?
+DNA is negatively charged due to the phosphate groups in its backbone, which carry a negative charge at physiological pH. (DNA charge, phosphate groups)
How does DNA charge affect its interactions with proteins?
+The negative charge of DNA influences how proteins bind to it, playing a critical role in processes like transcription and DNA replication. (protein interactions, transcription, DNA replication)
What is the significance of DNA charge in electrophoresis?
+In electrophoresis, DNA's negative charge causes it to migrate towards a positive electrode, allowing for the separation and analysis of DNA fragments. (DNA electrophoresis, fragment separation)
In conclusion, the charge of DNA is a fundamental property that underpins its structure, function, and interactions within the cell. By understanding DNA’s charge, we gain insights into its biological roles and its applications in biotechnology. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about molecular biology, grasping this concept is essential. (DNA charge, molecular biology, biotechnology applications)