xe orbital diagram

Understanding the Xe Orbital Diagram: A Comprehensive Guide
The Xe orbital diagram is a crucial concept in chemistry, particularly in understanding the electron configuration of the element Xenon (Xe). With an atomic number of 54, Xenon is a noble gas known for its stability and unique electronic structure. This guide will delve into the intricacies of the Xe orbital diagram, providing both informative and commercially relevant insights for chemistry enthusiasts and professionals alike.
What is an Orbital Diagram?

An orbital diagram visually represents the arrangement of electrons in an atom's orbitals. It uses boxes or lines to denote orbitals and arrows to indicate electron spin. For Xenon, understanding its orbital diagram is essential for grasping its chemical behavior and properties, such as its inertness and role in lighting technology (xenon flash lamps, keyword/title: xenon applications, chemical properties of xenon).
Xe Orbital Diagram Explained
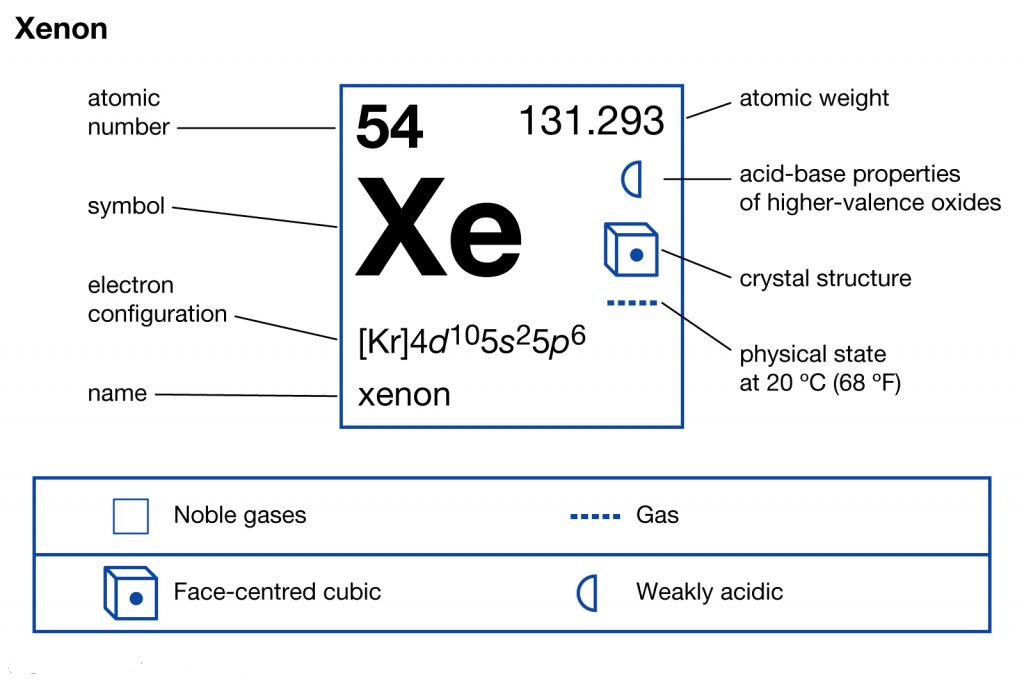
Xenon's electron configuration is [Kr] 4d¹⁰ 5s² 5p⁶. In its orbital diagram, electrons fill the orbitals according to the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund's rule. Here’s a breakdown:
- 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p: Filled orbitals inherited from Krypton ([Kr]).
- 4d¹⁰: Completely filled d-orbital.
- 5s²: Two electrons in the 5s orbital.
- 5p⁶: Six electrons in the 5p orbital, achieving a stable octet.
💡 Note: Xenon's fully filled 5p orbital contributes to its stability, making it a noble gas (keyword/title: noble gas stability, electron configuration).
Visualizing the Xe Orbital Diagram
Below is a simplified representation of Xenon's orbital diagram:
| Orbital | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|
| 1s | ↑↓ |
| 2s | ↑↓ |
| 2p | ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
| 3s | ↑↓ |
| 3p | ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
| 4s | ↑↓ |
| 3d | ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
| 4p | ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
| 4d | ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
| 5s | ↑↓ |
| 5p | ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |

Commercial Applications of Xenon
Beyond its theoretical importance, Xenon has practical applications in various industries. Its unique orbital configuration enables uses in:
- Lighting: Xenon flash lamps and arc lamps (keyword/title: xenon lighting, arc lamps).
- Medicine: Xenon anesthesia and imaging (keyword/title: xenon in medicine, medical applications).
- Space Exploration: Ion propulsion systems (keyword/title: xenon propulsion, space technology).
Checklist for Mastering Xe Orbital Diagram
- Understand the electron configuration of Xenon.
- Apply the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund's rule.
- Visualize the orbital diagram using boxes and arrows.
- Explore commercial applications of Xenon in lighting, medicine, and space technology.
By mastering the Xe orbital diagram, you gain insights into both the theoretical and practical aspects of this fascinating noble gas (keyword/title: noble gas properties, chemical stability).
What is the electron configuration of Xenon?
+Xenon’s electron configuration is [Kr] 4d¹⁰ 5s² 5p⁶.
Why is Xenon considered a noble gas?
+Xenon is a noble gas because its outermost orbital (5p) is fully filled, making it highly stable and unreactive.
What are the commercial uses of Xenon?
+Xenon is used in lighting (flash lamps, arc lamps), medicine (anesthesia, imaging), and space exploration (ion propulsion).