Op Amp Basics: Inverting vs Noninverting Explained

Operational amplifiers, or op amps, are fundamental building blocks in analog electronics, offering versatility in signal processing, amplification, and filtering. Understanding the difference between inverting and noninverting configurations is crucial for anyone working with op amps. This guide breaks down the basics, helping you choose the right configuration for your circuit design.
What is an Op Amp?
An operational amplifier is a high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and a single-ended output. It is designed to perform mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, integration, and differentiation in analog circuits. Op amps are widely used in audio equipment, sensors, and signal conditioning applications.
Inverting vs Noninverting Op Amp Configurations
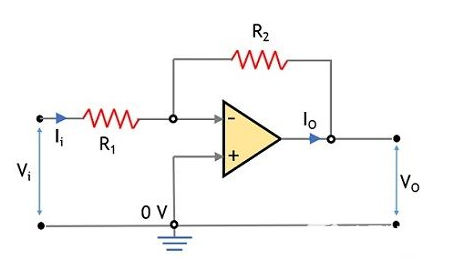
The two primary configurations of op amps are inverting and noninverting. Each has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications.
Inverting Op Amp Configuration
In the inverting configuration, the input signal is applied to the inverting terminal of the op amp. The output signal is 180 degrees out of phase with the input, meaning it is inverted.
- Key Features:
- Voltage Gain: Determined by the ratio of feedback resistor (Rƒ) to input resistor (R₁).
- Gain Equation: ( A_v = -\frac{R_f}{R_1} )
- Input Impedance: High, but depends on R₁.
- Voltage Gain: Determined by the ratio of feedback resistor (Rƒ) to input resistor (R₁).
📌 Note: The inverting configuration is ideal for applications requiring signal inversion, such as summing amplifiers and active filters.
Noninverting Op Amp Configuration
In the noninverting configuration, the input signal is applied to the noninverting terminal. The output signal is in phase with the input, meaning it is not inverted.
- Key Features:
- Voltage Gain: Determined by the ratio of (Rƒ + R₁) to R₁.
- Gain Equation: ( A_v = 1 + \frac{R_f}{R_1} )
- Input Impedance: Very high, making it suitable for high-impedance sources.
- Voltage Gain: Determined by the ratio of (Rƒ + R₁) to R₁.
📌 Note: The noninverting configuration is perfect for applications requiring signal amplification without phase inversion, such as buffer amplifiers.
Comparing Inverting and Noninverting Configurations

To help you decide which configuration to use, here’s a side-by-side comparison:
| Parameter | Inverting Configuration | Noninverting Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Relationship | Output is 180° out of phase | Output is in phase |
| Input Impedance | Depends on R₁ | Very high |
| Gain Equation | -\frac{R_f}{R_1} | 1 + \frac{R_f}{R_1} |

When to Use Each Configuration

- Inverting Configuration: Use when you need signal inversion, precise gain control, or summing multiple signals.
- Noninverting Configuration: Use when you need signal amplification without inversion, high input impedance, or buffering.
Checklist for Choosing the Right Configuration

- Determine Phase Requirement: Do you need the output in phase or inverted?
- Consider Input Impedance: Is your signal source high impedance?
- Calculate Gain: Use the appropriate gain equation for your design.
- Application Specifics: Match the configuration to your circuit’s purpose (e.g., summing, buffering, filtering).
The choice between inverting and noninverting op amp configurations depends on your circuit’s requirements. Inverting configurations offer signal inversion and precise gain control, while noninverting configurations provide in-phase amplification and high input impedance. By understanding these differences, you can design efficient and effective analog circuits tailored to your needs.
What is the main difference between inverting and noninverting op amps?
+The main difference lies in the phase relationship between input and output. Inverting op amps produce an output 180° out of phase, while noninverting op amps keep the output in phase with the input.
Which configuration has higher input impedance?
+The noninverting configuration has very high input impedance, making it suitable for high-impedance signal sources.
Can I use an inverting op amp for signal buffering?
+No, inverting op amps invert the signal, so they are not suitable for buffering. Use a noninverting configuration for signal buffering.
op amp configurations,inverting op amp,noninverting op amp,op amp basics,analog circuits,signal amplification,circuit design



